Magnetic resonance studies of bone marrow hematopoiesis
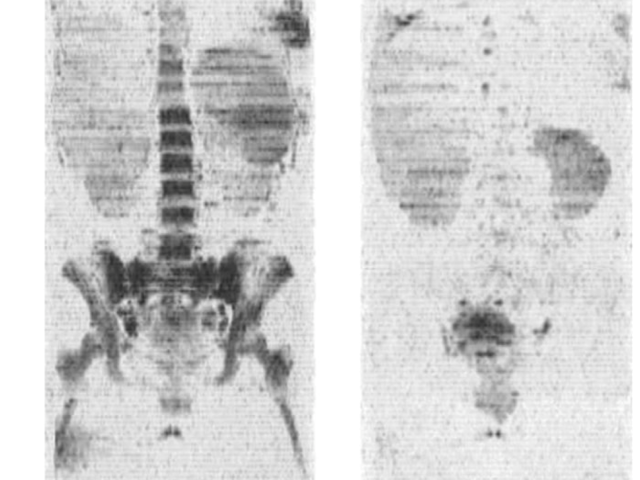
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH), R01EB002070 The Ballon lab has developed new methods for whole-body imaging of metastatic disease in oncology. The lab introduced a rapid, whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for leukemia and metastatic cancers including prostate and breast cancer. The method is based, in part, on measurements of intracellular water self-...
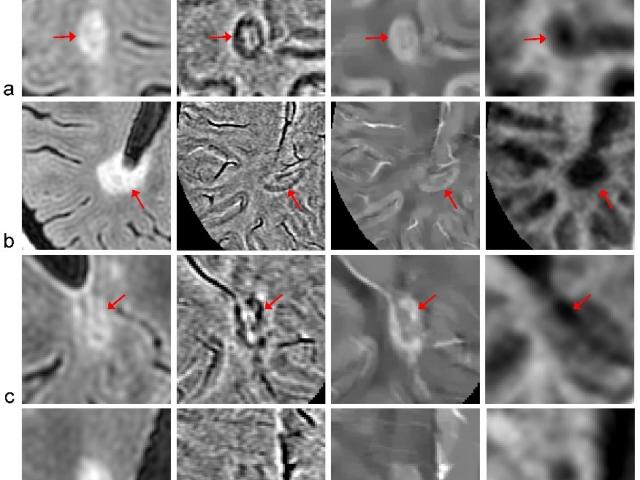
Techniques for magnetic resonance microscopy
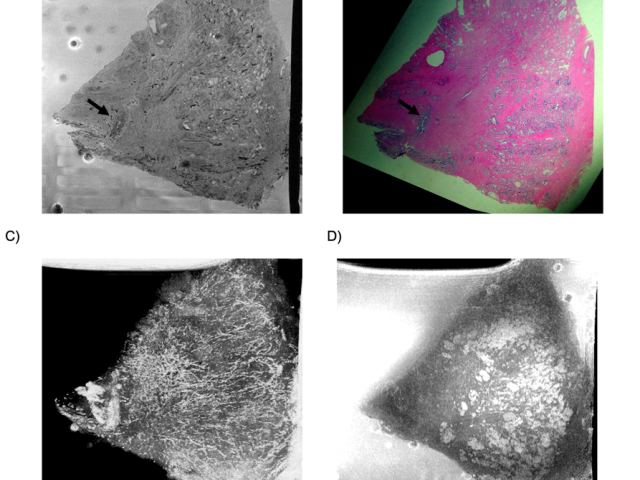
Award or Grant: Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) Research and Education Foundation Roentgen Resident/Fellow Research AwardResidents and fellows rotating through the Ballon lab have developed methods for imaging specimens using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at high spatial resolution. In one project, the lab achieved high-contrast, high-resolution MR microscopy (MRM) of murine...
Multiparametric MRI imaging of CLN2 (a form of Batten disease)
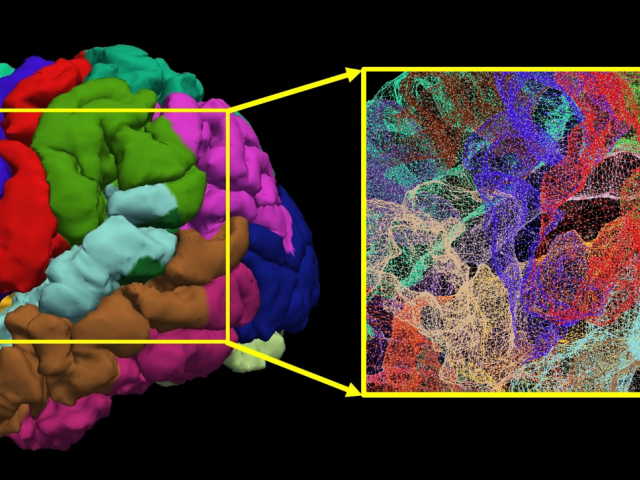
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01NS061848, U54NS065768). The Lysosomal Disease Network (U54NS065768), which is part of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (RDCRN). Late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (LINCL) is a rare uniformly fatal pediatric neurodegenerative disease resulting from a mutation...
DCE-MRI of osteogenic and Ewing’s sarcomas
As a post-doctoral fellow, Dr. Dyke developed the first technique at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) to non-invasively assess the grade of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in pediatric subjects with osteogenic or Ewing’s sarcomas using dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE)-MRI. This technique is still in use and lets the orthopedic surgeon determine tumor response to chemotherapy prior to...
Thermoacoustic SAR monitoring tool (TASAR)
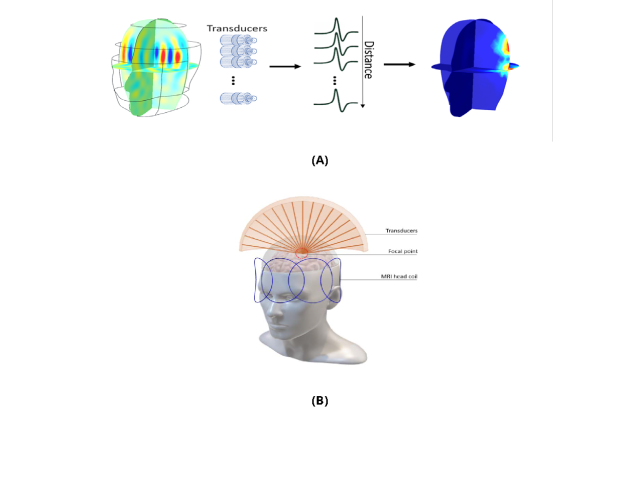
The rapid and successful advancement in ultra-high field (UHF) magnetic resonance (MR) scanners (7 tesla (T) or higher) has led to improvement in the spatial and temporal resolution and the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) per unit time of MR images. However, imaging of human-sized objects at high frequency (Larmor frequency of 1H ≥ 300 MHz) presents a key limitation quantified by an excessive...
Impact of high LET radiation on host immune response to augment immunotherapy
Award or Grant: SPORE in Prostate Cancer Developmental Research Program Award Local radiotherapy has been recognized as a powerful inducer of acute inflammation and immunogenic cell death. Seminal work implicating T cells in the response to local radiotherapy (RT) was reported years ago. But it was only recently that mechanisms conveying immunogenicity of irradiated tumor cells have been...
DOTA-based pre-targeting of alpha emitters
Antibody-based targeting provides superior specificity for radionuclide therapy. However, it suffers from low absorbed dose compared to external beam radiotherapy and normal tissue toxicity due to the slow circulation and tumor uptake of antibodies. Pre-targeted radioimmunotherapy separates the slow antibody targeting phase from rapid delivery of the radionuclide by small anti-chelate ligands....
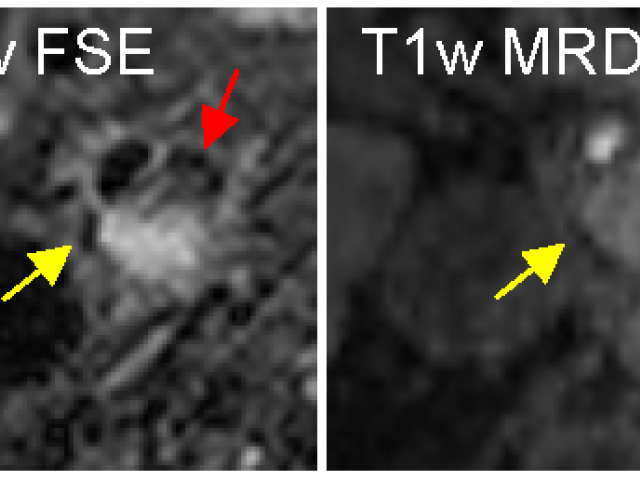
Quantitative MRI of lesion iron and myelin repair
Award or Grant: National MS Society RR-1602-07671The Nguyen Lab’s objective is to establish the association between lesion iron and subsequent myelin recovery in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. The lab will develop quantitative and reliable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods including myelin water fraction (MWF) mapping and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) to measure iron and...
Quantitative susceptibility mapping of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage
Award or Grant: R21 NS116516; R01 NS123576-01A1 (not yet funded)The team’s key objective is to use quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) to establish reliable, noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for identification and risk stratification of unstable carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Currently, decisions about carotid revascularization to prevent stroke, such as carotid endarterectomy...
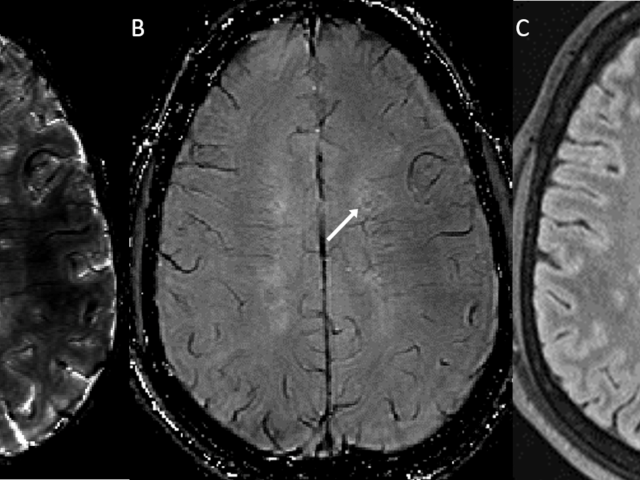
No-Gd MRI for monitoring disease status in multiple sclerosis
Our patients objective is to eliminate gadolinium (Gd) injections in routine follow-up magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of multiple sclerosis (MS) using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a direct response to calls issued by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to re-evaluate repetitive Gd administration to patients. We have pioneered QSM...