Noninvasive measurement of oxygenation using quantitative susceptibility mapping
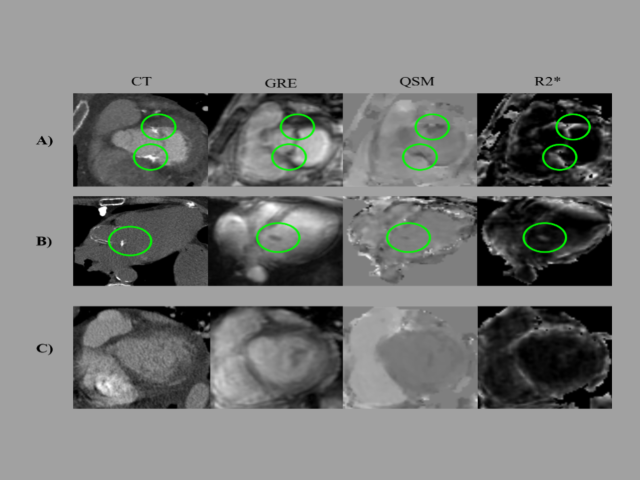
The goal of this research is to develop cardiac quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique, for non-invasive measurement of blood oxygen saturation in the heart—an index that strongly predicts clinical outcomes but currently requires invasive testing. To do so, blood oxygenation on QSM will be validated in relation to invasively measured...
Assessment of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) volumetrics and kinetics for drug delivery
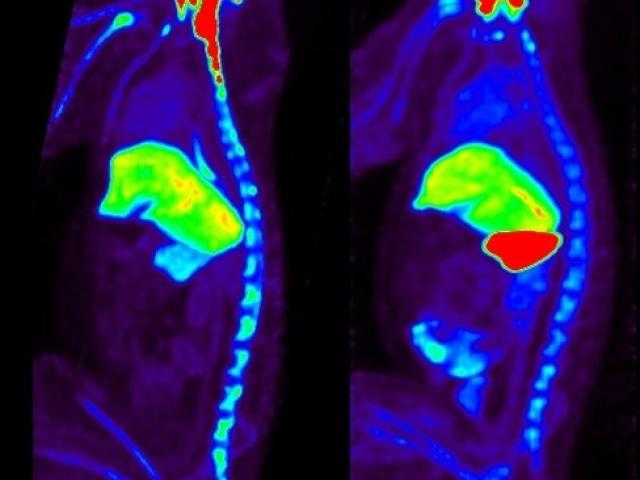
Delivery of various drugs in both intrathecal and intracisternal spaces are being used to treat a myriad of diseases. Knowledge of the rate of drug delivery to each region in the brain via the CSF space may be estimated by using MRI. Our lab published the first time course results of intrathecal gadolinium uptake in CSF and brain regions in normal control subjects using high resolution MRI. In...
Multiple sclerosis lesion magnetic susceptibility activity
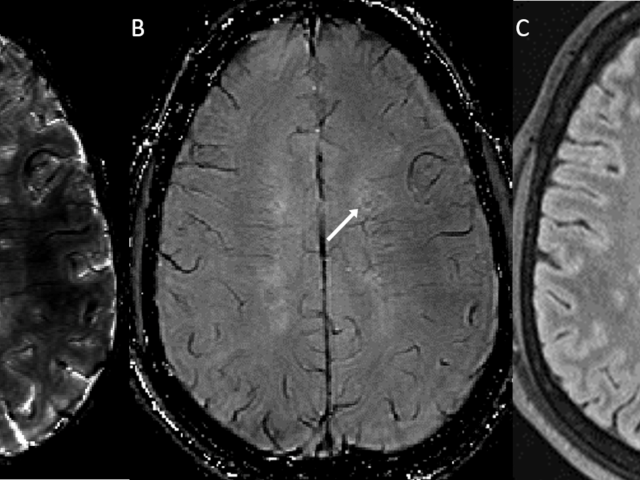
The long-term objective of this project is to improve the ability to monitor inflammatory and neurodegenerative processes in multiple sclerosis (MS) for effective diagnosis and treatment. The specific goal: to establish the time course of magnetic susceptibility of lesions as a sensitive probe of demyelination and iron content associated with inflammatory processes. Currently, gadolinium...
Quantitative methods for preclinical Ac-225 imaging
Award or Grant: Radiology/Citigroup Biomedical Imaging Center Pilot AwardIt is well documented that molecularly targeted radiotherapy, such as pre-targeted radioimmunotherapy, can be optimized on a patient-specific basis with pre-therapeutic imaging and dosimetry. This can be carried out with theranostic isotopes such as the beta/gamma emitter lutetium (Lu)-177, or with therapeutic isotopes in...
Rapid noninvasive whole-body imaging of AAV gene transfer vectors
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01) EB027918Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a widely used vector for gene delivery. Its in vivo distribution, though, has not been well characterized, as most studies are based on rodent biopsy or necropsy data. The distribution is also dependent on route of administration and pre-existing immunity. The goal of this project was to develop an...
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for the study of normal pressure hydrocephalus
In this research project, the Kovanlikaya group used advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), arterial spin labeling (ASL), phase contrast cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow measurement, and structural volumetric MRI to develop quantitative criteria to diagnose normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) patients more precisely.
Normative data from advanced MR techniques of the brain
The aim of this project was to establish a standard normative database of advanced magnetic resonance (MR) techniques, including but not limited to diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), MR perfusion, and 3D volumetric studies to use for diagnostic and clinical research on the aging adult brain and/or various disease states. This project will also ensure ongoing comparability (i.e., quality assurance (...
DTI fiber tractography identifying the thalamic ventralposterolateral nucleus
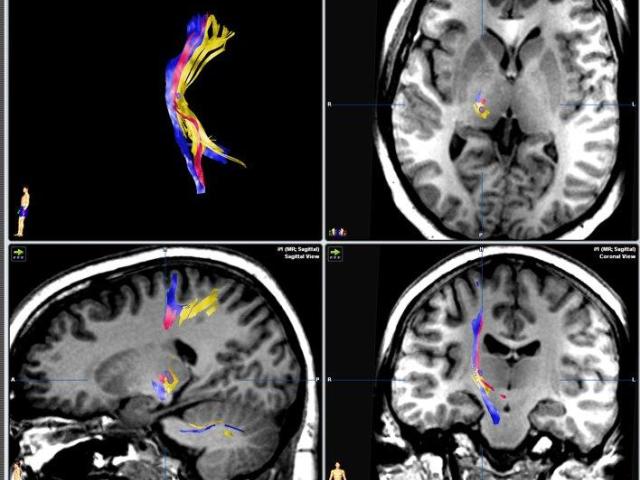
The purpose of this project was to preoperatively identify the thalamic ventroposterolateral nucleus by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-fiber tractography and confirm it intraoperatively. A variety of pain syndromes have been treated successfully with deep brain stimulation (DBS) by targeting the thalamic ventroposterolateral (VPL) nucleus. We found that DTI has the potential to identify the...
Retrospective analysis of quantitative imaging biomarkers as predictors of brain tumor clinical outcome and pathology
Although advanced imaging techniques provide quantitative, metabolic and functional data about brain tumors, it is evident that, as yet, there is no single technique that can offer a complete picture of brain tissue and tumor characterization. By generating a database of all brain tumor patients and their radiological and pathological studies and genetic biomarkers, we perform hypothesis-driven...
Major cyclotron upgrades and refurbishment
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH), S10OD030447The lab’s research efforts using iodine (I)-124 positron emission tomography (PET) to image viral vectors require a cyclotron for production of the radioisotope. The cyclotron, in turn, requires special targetry to produce iodine (I)-124. The research resources at the Citigroup Biomedical Imaging Center (CBIC) include a 19 MeV...