Area of investigation
Our research work focuses on developing precision nanomedicines, with the long-term goals of achieving a more specific and effective drug delivery for the treatment of different type of cancers. In my lab, we design on-demand nanocarriers displaying organ-specific targeting and/or retention properties to improve the safety and efficacy of chemotherapeutic treatments. Our peptide-based delivery systems promote drug targeted delivery, tissue penetration, and tumoral uptake and retention, for cancer imaging and therapy.
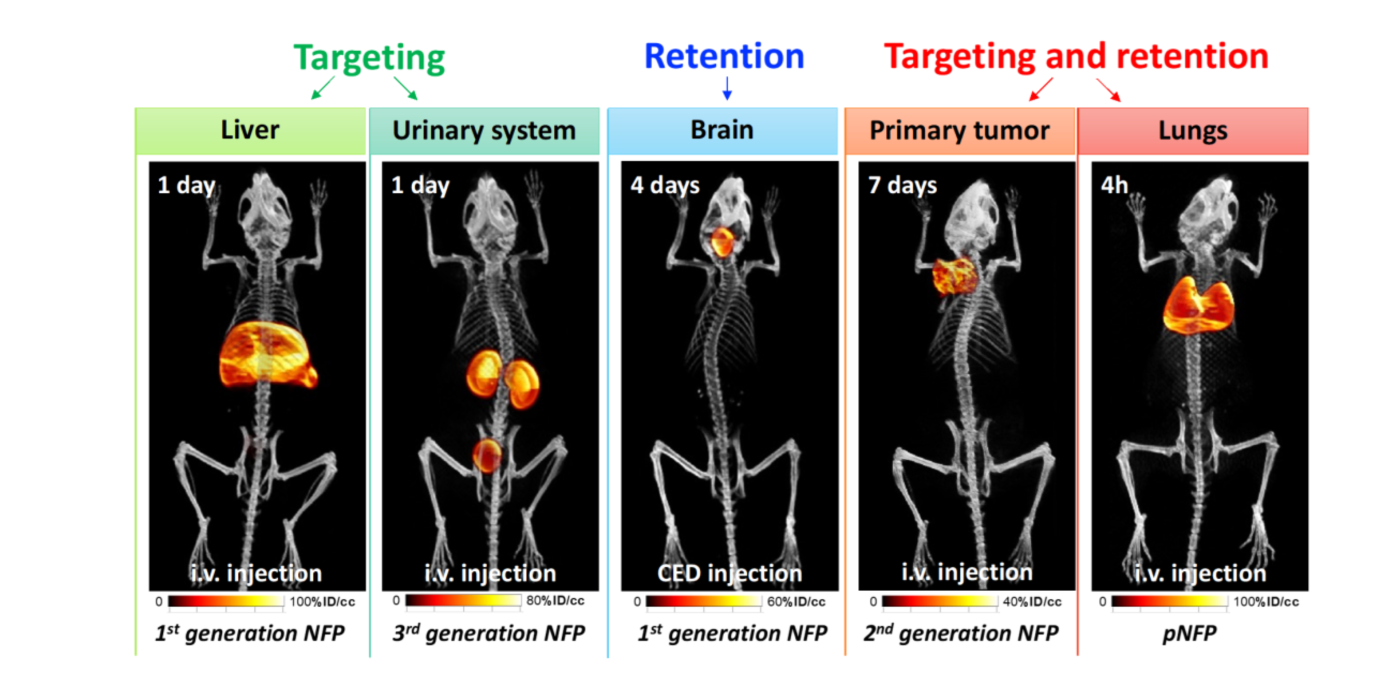
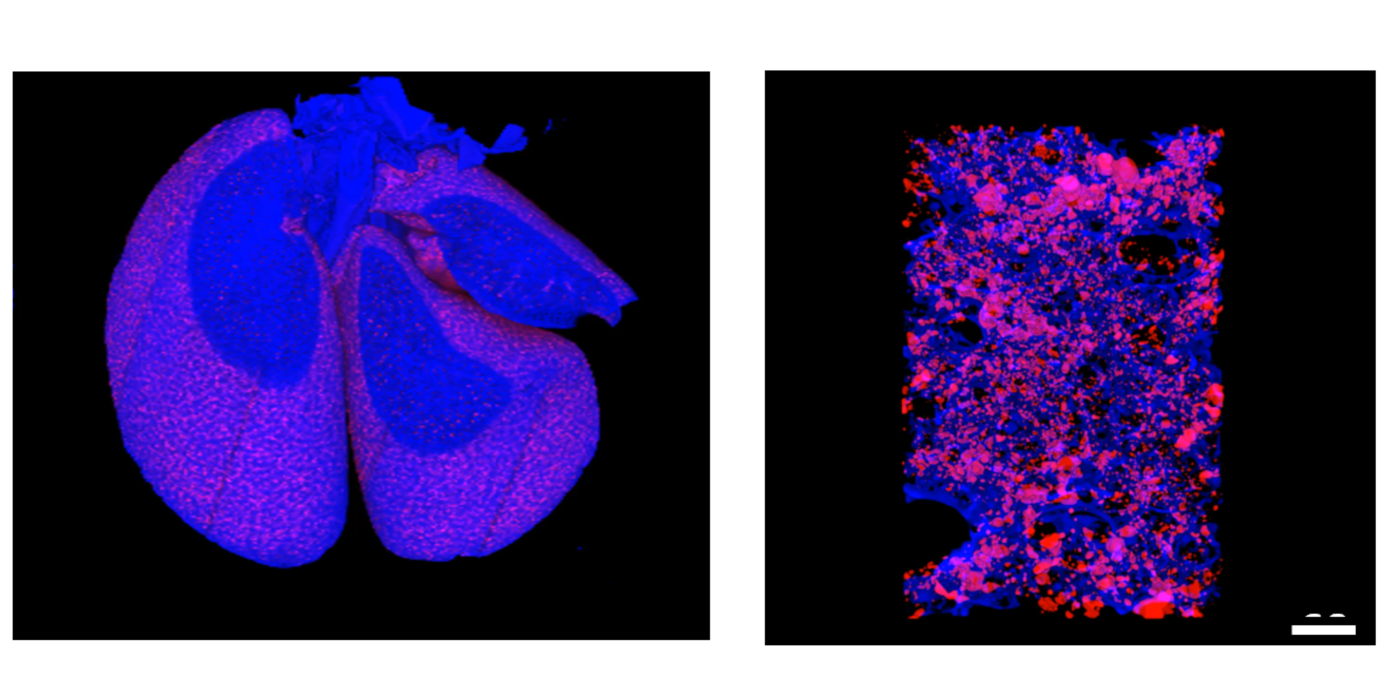
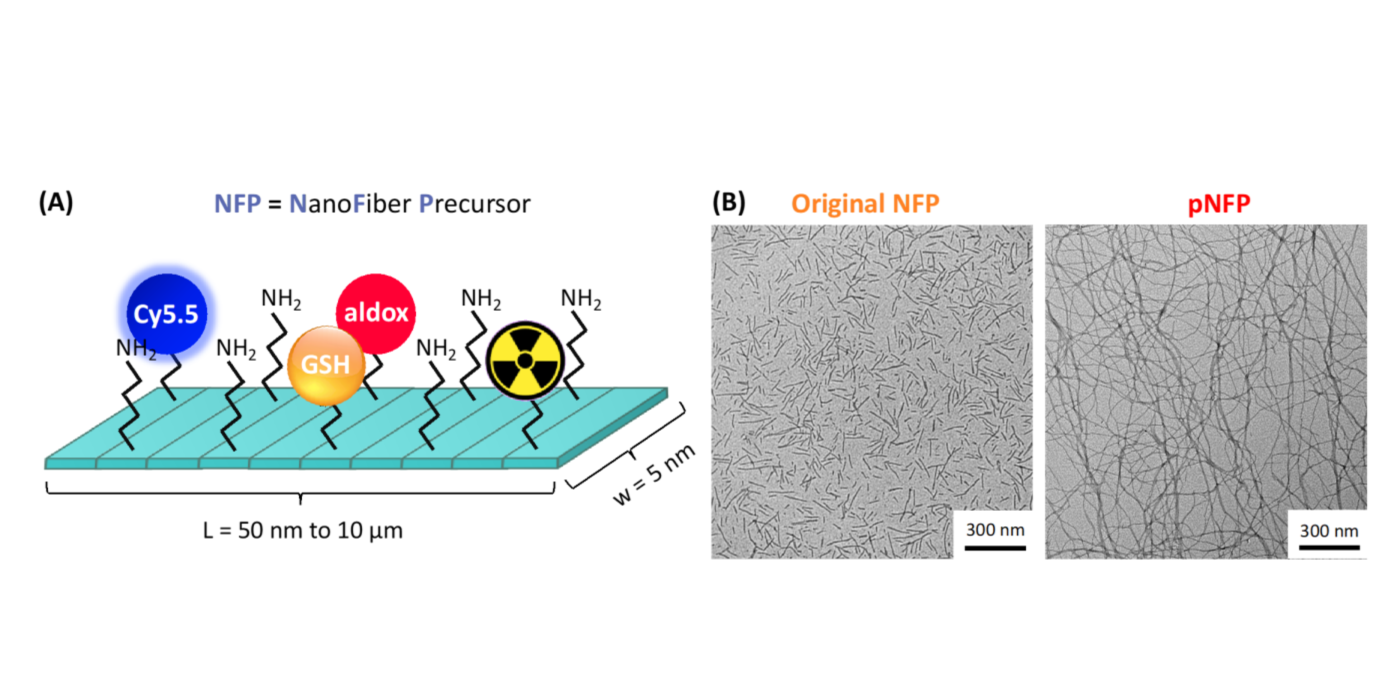
Currently, most nanotechnology cancer therapies focus on the treatment of primary tumors, but it is important to leverage the potential of nanomedicine to combat cancer spread at each stage of the metastatic process. With a keen intertest in developing innovative therapeutic approaches for treating pulmonary metastases, we have notably designed a new generation of nanofibers (pNFP) displaying preferential lung-targeting and -retention properties. The nanofibers display a unique 2D single layer structure with a very high aspect ratio (5 nm in width and 10 μm in length) and carries multiple positive charges that promote lung affinity and uptake with a limited off-target accumulation in other organs. Multiple pNFP can also rearrange into a large interfibril network which favors the local retention in the lung tissue via mechanical trapping in the deep alveolar areas. When used as delivery platform, the nanofibers will serve as a drug depot that supplies a continuous drug flow for a more effective long-term treatment. The combination of organ-targeting and -retention properties will allow a reduction in the applied drug dosages to reach a better therapeutic effect and minimize the chemotherapy-associated morbidity and mortality. With additional advancements, the nanofiber technology could be further transposable to locally deliver and release various drug molecules for treating other lung malignancies, including cystic fibrosis, pleural effusion, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Publications
2022
- Maurizi L, Bellat V, Moreau M, De Maistre E, Boudon J, Dumont L, Denat F, Vandroux D, Millot M. Titanate nanoribbon-based nanohybrid for potential applications in regenerative medicine. RSC Advances. 2022;12(41):26875-81. PMID: 36320832.
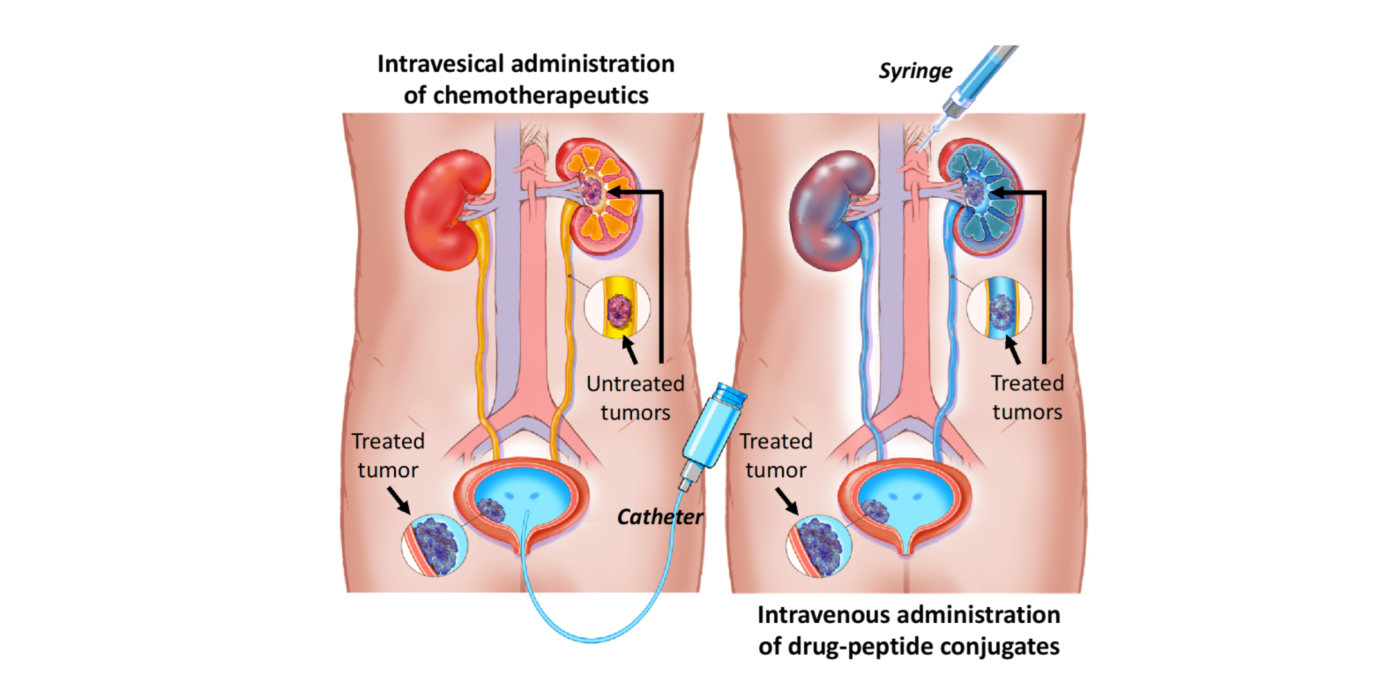
- Bellat V, Michel AO, Thomas C, Stokol T, Choi BB, Law B. A Urinary Drug-Disposing Approach as an Alternative to Intravesical Chemotherapy for Treating Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022;82(7):1409-22. PMID: 35039320.
2020
- Bellat V, Alcaina Y, Tung CH, Ting R, Michel AO, Souweidane M, Law B. A combined approach of convection-enhanced delivery of peptide nanofiber reservoir to prolong local DM1 retention for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma treatment. Neuro Oncol. 2020;22(10): 1495-504. PMID: 32301996.
- Bellat V, Verchere A, Ashe SA, Law B. Transcriptomic insight into salinomycin mechanisms in breast cancer cell lines: synergistic effects with dasatinib and induction of estrogen receptor beta. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):661. PMID: 32678032.
- Stokol T, Wan C, Blakely R, Bellat V, Law B. Aldoxorubicin-loaded nanofibers are cytotoxic for canine mammary carcinoma and osteosarcoma cell lines in vitro: A short communication. Res Vet Sci. 2020;128:86-89. PMID: 31760317.
2019
- Tosi U, Kommidi H, Bellat V, Marnell CS, Guo H, Adeuyan O, Schweitzer ME, Chen N, Su T, Zhang G, Maachani UB, Pisapia DJ, Law B, Souweidane MM, Ting R. Real-time, in vivo correlation of molecular structure with drug distribution in the brain striatum following convection enhanced delivery. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(5):2287-89. PMID: 30838861.
2018
- Bellat V, Ting R, Southard TL, Vahdat L, Molina H, Fernandez J, Aras O, Stokol T, Law B. Functional Peptide Nanofibers with Unique Tumor Targeting and Enzyme-Induced Local Retention Properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(44). PMID: 30505260.
- Singh R, Bellat V, Wang M, Schweitzer ME, Wu YL, Tung CH, Souweidane MM, Law B. Volume of distribution and clearance of peptide-based nanofiber after convection-enhanced delivery. J Neurosurg. 2018;129(1):10-18. PMID: 28885119.
2017
- Lee HH, Bellat V, Law B. Chemotherapy induces adaptive drug resistance and metastatic potentials via phenotypic CXCR4-expressing cell state transition in ovarian cancer. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0171044. PMID: 28196146.
2016
- Bellat V, Lee HH, Vahdat L, Law B. Smart Nanotransformers with Unique Enzyme-Inducible Structural Changes and Drug Release Properties. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(6):2040-9. PMID: 27180972.
2015
- Bellat V, Chassagnon R, Heintz O, Saviot L, Vandroux D, and Millot N. A multi-step mechanism and integrity of titanate nanoribbons. Dalton Transactions. 2015;44(3):1150-1160. PMID: 25412498.
- Papa AL, Boudon J, Bellat V, Loiseau A, Bisht H, Sallem F, Chassagnon R, Berard V, and Millot N. Dispersion of titanate nanotubes for nanomedicine: comparison of PEI and PEG nanohybrids. Dalton Transactions. 2015;44(2):739-746. PMID: 25408156.
Patents
2020
US patent: Law B, Bellat V, Choi B, Peptide-linked drug delivery system, Patent disclosed to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, application number US17/556,714.
2018
US patent: Law B, Tung CH, Bellat V, Enzyme-responsive peptide nanofiber compositions and uses thereof. US20180296697A1 and WO2017059338A1.
2014
FR patent: Vandroux D, Millot N, Bellat V, Titanate-based nanostructures for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. WO 2014/079890A4.