MRI method for quantitatively mapping cerebral microbleeds
The objective of this research is to develop a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method for mapping iron deposits in cerebral microbleeds (CMB). There is significant scientific and clinical interest in studying CMB, which are focal lesions of hemosiderin deposits from red blood cells leaked out of small brain vessels. CMB have become an important concern for managing stroke patients,...
Heritability and cognitive implications of structural-functional connectome coupling
Award or grant: National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Mental Health (NIH/NIMH): 1RF1MH123232The human brain is an unimaginably complicated system of interconnected neurons capable of complex thought, emotion and behavior. Macroscale white matter connections quantified via the structural connectome (SC) act as the backbone for the flow of functional activation, which can be...
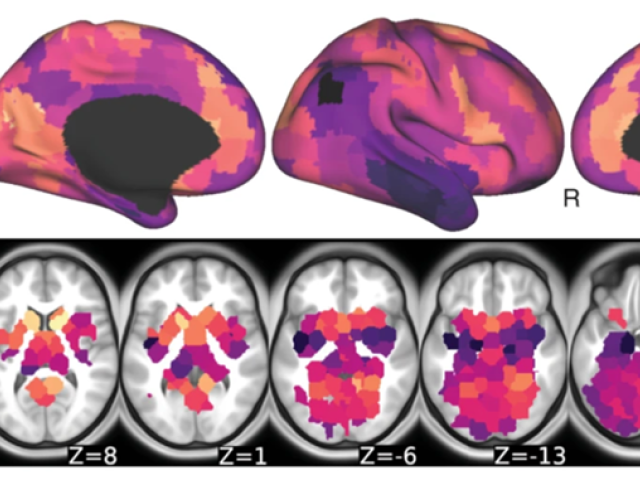
Hierarchical structure of the brain's large-scale networks
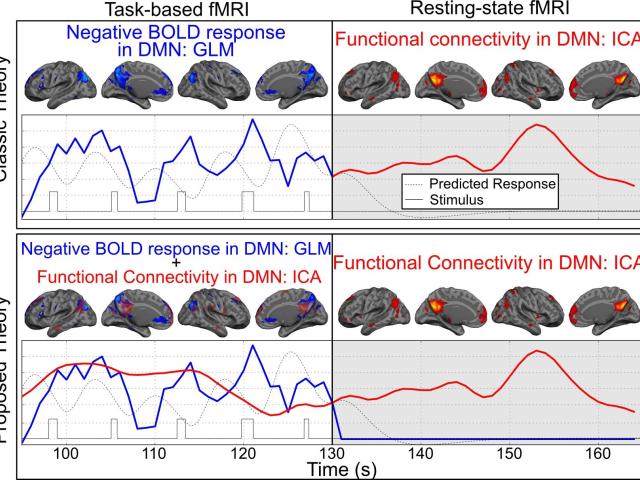
The default mode network’s (DMN’s) topography can be obtained using two different functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) techniques: 1) spontaneous, but organized, synchrony in the low-frequency fluctuations of resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI), known as “functional connectivity”; 2) consistent, robust deactivations in task-based fMRI (tb-fMRI), here referred to as the negative blood-oxygenation...
PET measures of CSF clearance in preclinical AD
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute on Aging (NIA) 1RF1 AG057570 (09/15/17-03/31/22). This project is designed to develop and test a positron emission tomography (PET) based ventricular cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) clearance technology invented by the PI in the characterization of amyloid accumulation using 11C-Pittsburgh compound B (PiB) PET imaging.
Identification of dysregulated lipid pathways for biomarker and therapeutic target discovery
To test the hypothesis that manipulation of brain lipid content alters brain lipidome and cognitive function in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), we propose to genetically alter the synthetic enzyme, Acyl CoA Synthetase 6 (Acsl6), a key mediator of polyunsaturated fatty acid enrichment in the brain— especially docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) across multiple lipid classes—in mouse models of AD...
Gradient-echo spectroscopic imaging study of saturated fat and breast cancer
Award or Grant: R01CA219964, National Cancer Institute (NCI) (02/01/18 – 01/31/23). Description: The role of breast fatty acid composition in breast cancer development, in conjunction with breast density and body mass index, has not been fully investigated. The central hypothesis of the Kim lab is that its recently developed gradient-echo spectroscopic imaging method can be used to investigate...
Establishment of efficacy of DOTA-based pretargeted radioimmunotherapy with a bivalent radiohapten for enhanced therapeutic indices
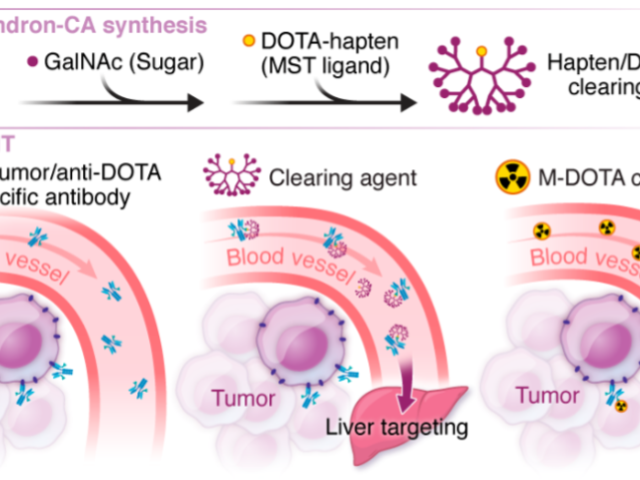
We are currently developing a novel bivalent radiohapten class that we refer to as “gemini” for “twin haptens” to achieve improved therapeutic indices (TIs) via cooperative binding at intratumoral bispecific anti-tumor/anti-DOTA antibody (BsAb).
Assessment of placental perfusion and oxygenation using ASL and QSM
In the management and treatment of pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction (FGR) and preeclampsia (PE) due to placental insufficiency, early and reliable detection is critical. For, once clinically evident, those pathological changes are irreversible. But there is no validated in-vivo method that can be routinely used in the clinic for non-invasive assessment of placental function. In...
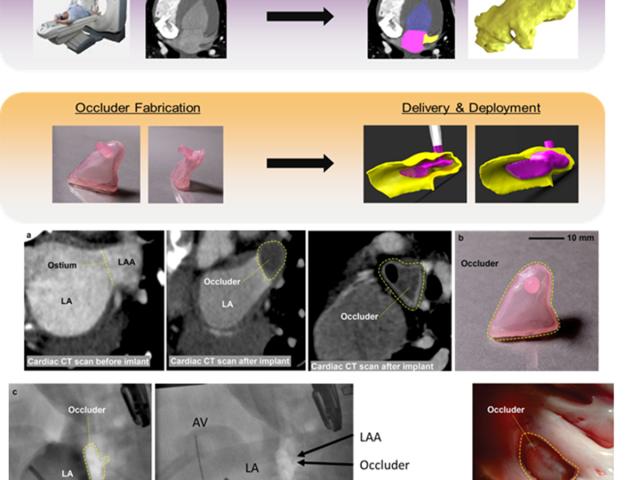
Patient-specific left atrial appendage (LAA) occluder
The goal of this project was to develop a patient-specific occluder for the left atrial appendage (LAA), as a stroke prevention device for atrial fibrillation (AF) patients. The lab developed a workflow to design and fabricate personalized devices using 3D printing. AF, which promotes blood clots, increases stroke risk five to seven times over. Warfarin, an oral anti-coagulant, is the mainstay of...
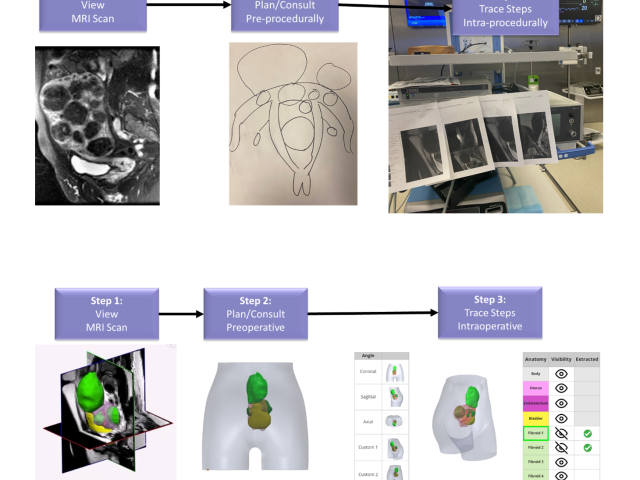
Mixed reality patient counseling/surgical guidance for uterine fibroid treatment
Most benign tumors are uterine fibroids in women, especially African American women. Today, doctors counsel women using flat magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images, but fibroids can grow on multiple uterine planes, and 2D imaging does not accurately allow optimized planning and intraoperative guidance. Our technology brings MRI into the modern age by leveraging deep learning algorithms to...