Fluid mechanics approach to tissue perfusion quantification in MRI
Our overall goal is to develop a fluid mechanics approach to studying tracer transport through tissue for perfusion quantification in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is termed as quantitative transport mapping (QTM). Current/traditional perfusion quantification in MRI and medical imaging in general is based on Kety's method that assumes the same arterial input globally into all voxels in...
Pharmacokinetic PET modeling of 18F-BPA-fructose in glioblastoma multiforme in BNCT
Dr. Dyke’s Ph.D. work focused on compartmental modeling of a novel tumor- specific PET tracer used for dose planning of radiation therapy. He implemented novel pharmacokinetic compartmental model fitting of metabolic uptake of this tracer in subjects presenting with glioblastoma multiforme brain tumors prior to therapy. Uptake results were used to produce dose treatment plans prior to a novel...
Hypertension, brain clearance and markers of neurodegeneration
Age is the strongest risk factor for brain diseases related to accumulation of misfolded proteins and also the risk for vascular diseases. So far, there is little evidence that excessive production of proteins forming brain deposits in neurodegenerative conditions contributes to their pathology. A reduced clearance of brain waste has emerged as a possible factor underlying disease development....
CSF clearance in sporadic Alzheimer's disease
A longitudinal study of elderly normal control and mild cognitive impairment subjects to examine the clearance deficit in early stages of Alzheimer's disease, association with brain amyloid burden, and features of neurodegeneration (atrophy and cognitive function).
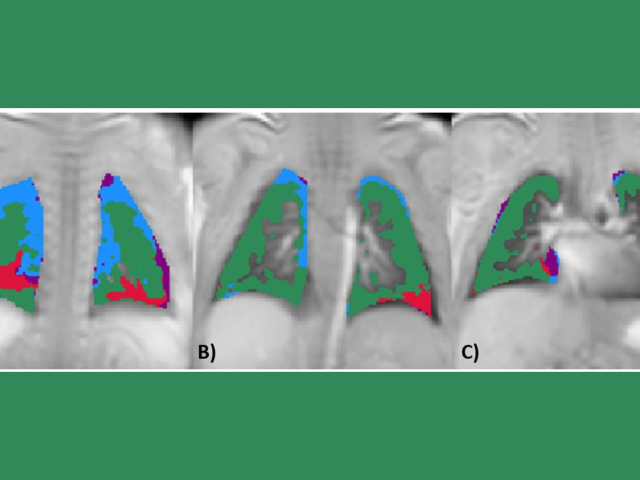
Phase-Resolved Functional Lung (PREFUL) MRI of Ventilation and Perfusion in Premature Infants
We are pioneering the use of a novel phase-resolved functional lung (PREFUL) MRI protocol that does not require sedation, contrast administration, or radiation to measure ventilation, perfusion defects, and pulmonary perfusion in this vulnerable infant population. This information on lung function cannot be achieved by any other means. Our work at the new Alexandra Cohen Hospital for Women and...
Imaging tumor cellular and vascular properties
Assessment of cancer treatment requires an effective non-invasive method of measuring both the vascular and cellular changes induced by therapies. Our central hypotheses is that dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurement, using the active contrast encoding (ACE) MRI method, can provide a fast and quantitative means to assess both anti-angiogenic and cytotoxic...
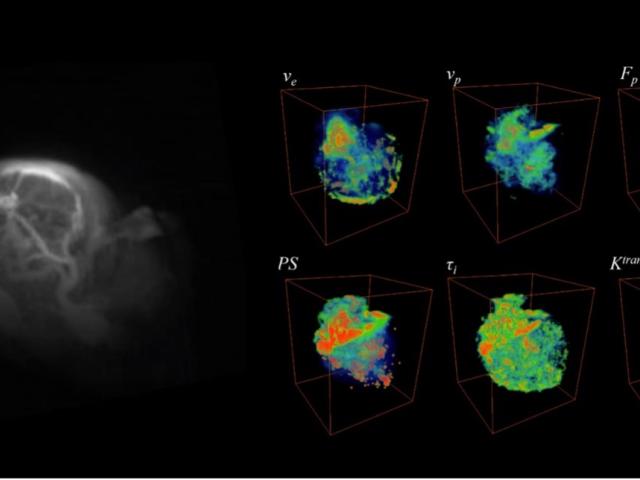
Rapid in vitro quantification of sensitized gadolinium chelates
Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI has been used to measure important tumor microenvironmental parameters, such as plasma flow (Fp), vascular permeability surface area product (PS), vascular plasma volume fraction (vp), and extravascular extracellular volume fraction (ve), that can be used for diagnosis of cancer as well as for prediction and monitoring of treatment response. However, accurate...
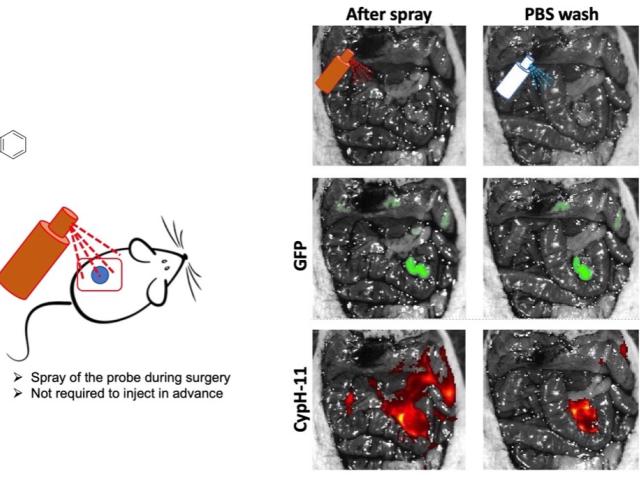
Instantaneous tumor spray for real-time surgical guidance
Early-stage ovarian cancer is typically asymptomatic. Despite successful initial treatments, 80–90% of women with advanced cancer experience tumor recurrence. For real-time ovarian cancer surgeries, we have identified an optimized pH-sensitive near-infrared fluorogenic dye (CypH-11) which remains non-fluorescent in normal tissues but becomes fluorescent immediately upon contact with cancer tissue...
In vivo local drug release and impact on the therapeutic efficacy
The main limitations of the use of nanoparticles as drug delivery platform for cancer treatment are the inconsistent deep-tissue targeting resulting in a lack of tumor penetration, and the incomplete drug release on tumor site leading to a depreciation of safety and therapeutic efficacy. The nanofiber technology allows to carry more drugs to the metastatic lung tumors and favors the local...
Combination of the nanofiber technology with radiation therapy
Both chemotherapy and radiation therapy (RT) are frequently used in the curative-intent, adjuvant therapy, and palliative treatment of lung metastases. However, these approaches suffer from lack of specificity and high toxicity leading to treatment failure and/or resistance, disease relapse, and adverse effects. For instance, a more aggressive and multidisciplinary strategy need to be considered...