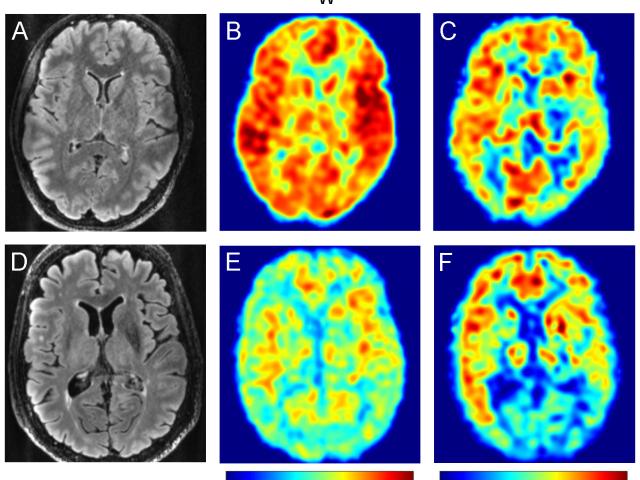
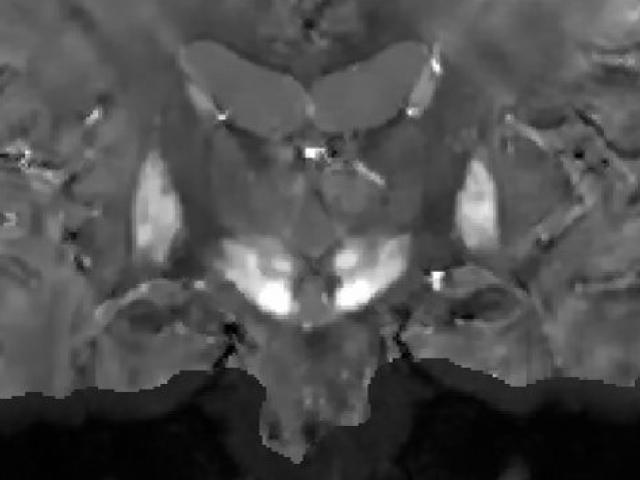
Quantitative permeability mapping of water exchange across the blood-brain barrier in normal aging and AD
Award or Grant: R01 AG077594-01 (not yet funded)The team’s objective is to develop quantitative permeability mapping (QPM) of kW, the water exchange rate across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), for the detection and quantification of BBB impairment in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to map BBB permeability to an...
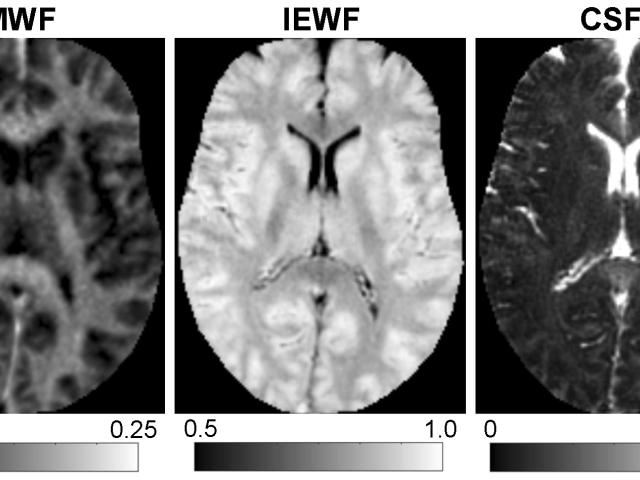
Quantitative mapping of parenchymal CSF fraction in Alzheimer’s disease
Award or Grant: R01 AG079326-01The team’s objective is to develop a new imaging method for quantitative mapping of parenchymal cerebrospinal fluid fraction (CSFF). The team’s preliminary data showed CSFF increased in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and was associated with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bulk flow reduction and decreased ventricular CSF clearance. More importantly, increased CSFF correlated...
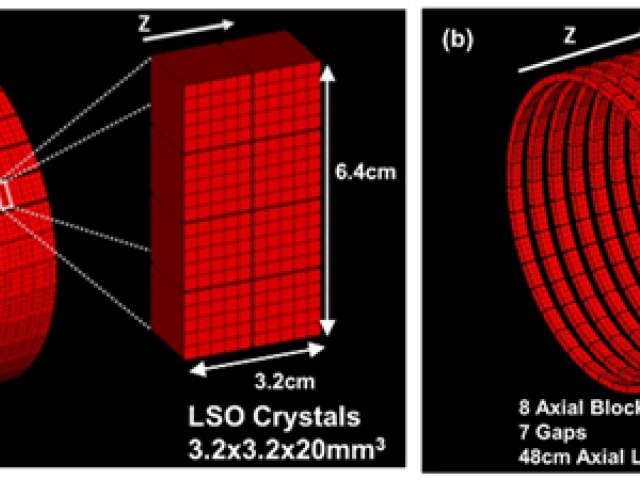
Long-axial field-of-view PET
Positron emission tomography (PET) sensitivity and applications (in particular those requiring simultaneous imaging of distant organs) are hindered due to the scanner limited axial field-of-view (AFOV), typically <26cm. A longer AFOV will create new opportunities to extend PET clinical and research applications to perform studies that benefit from simultaneous imaging of distant organs, such...
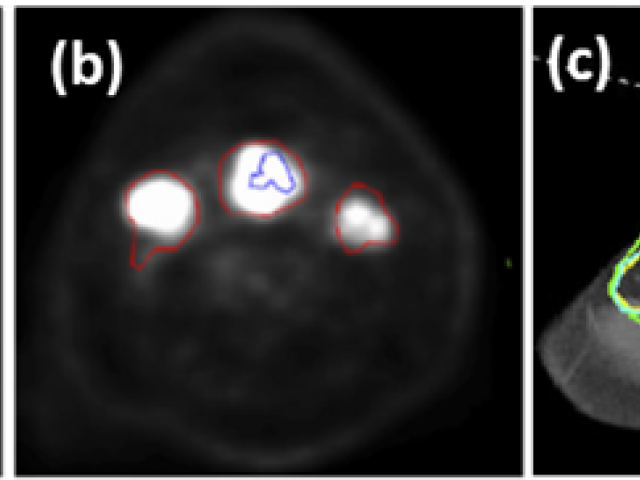
Hypoxia imaging
By using 18 fluorodeoxyglucose (F)-labeled fluoromisonidazole (FMISO) PET imaging, Dr. Sadek Nehmeh assessed tumor hypoxia imaging in head-and-neck and lung cancer patients undergoing chemoradiation. In this work, compartmental kinetic modeling of FMISO-dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) images generated parametric maps of both tumor perfusion and tumor hypoxia. Identifying different...
Quantitative mapping of substantia nigra iron in Parkinson’s disease
The long-term objective of this project is to develop noninvasive, robust, sensitive and accurate midbrain iron mapping for Parkinson's disease (PD). PD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dopaminergic neuron loss in the substantia nigra pars compactor (SNc) and consequent motor disorders. While the neurodegenerative processes in PD may be multifactorial, prooxidant iron elevation in...
QSM to guide iron chelating therapy in transfusional iron overload
The overall objective of this research is to improve the safety of iron-chelating therapy (ICT) in patients with transfusional iron overload by developing accurate non-invasive measurement of the liver iron concentration (LIC), the best measure of the body iron burden in all forms of systemic iron overload. The lab’s scientific premise is that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), using quantitative...
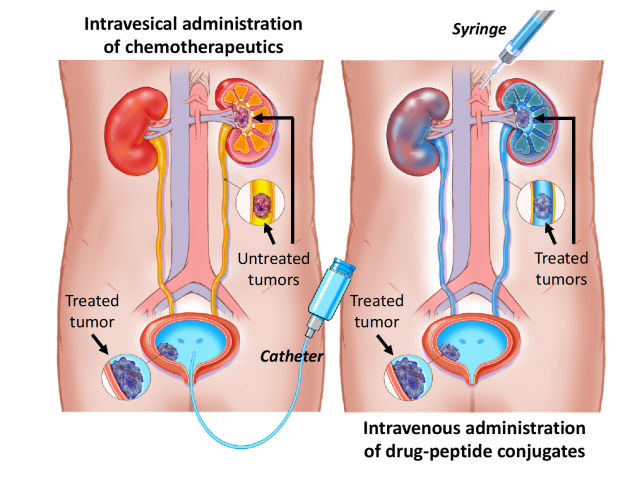
A urinary drug-disposing approach as an alternative to intravesical chemotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
This project involves a proposal to use a small bio-inert peptide as an alternative strategy to intravesical chemotherapy (ITC) for improvement of bladder cancer treatment and survival outcomes. When using the peptide as a drug delivery platform, the chemotherapeutics will be eliminated exclusively via renal clearance with minimal deposition in other main organs. This urinary drug disposing...
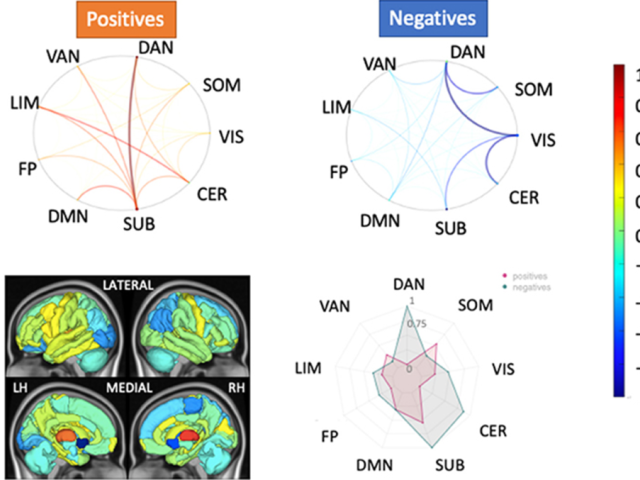
Quantifying the role of the connectome in resiliency to multiple sclerosis
Award or grant: National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NIH/NINNDS): R21 NS104634-01Multiple Sclerosis (MS) damages white matter pathways that connect brain regions, i.e., the structural connectome (SC), disrupting flow of electrical signals, i.e., the functional connectome (FC), causing cognitive and physical disability. However, the burden of...
Clinical summer immersion for biomedical engineering Ph.D. students
We propose a summer clinical immersion program at the Weill Medical College of Cornell University that brings Biomedical Engineering (BME) Ph.D. students from the Ithaca Engineering College Campus to the New York City Medical College Campus for dedicated intensive clinical exposure in the summer between their first and second year of graduate training. Each student will take bioethics lectures;...
Quantifying the link between connectivity disruption and patient dysfunction and disability in stroke
Award or grant: Leon Levy Foundation FellowshipUnderstanding the organization of the white matter structural connectivity (SC) network in the human brain is essential for elucidating the brain-behavior relationship and its dysfunctions in various diseases and injury. Our lab’s Network Modification (NeMo) Tool uses a large set of healthy tractograms to investigate these relationships by measuring...