CSF clearance with 11C-butanol PET predicts amyloid deposition
Awards or Grants: R56 AG058913, National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Aging (NIH/NIA) (09/15/18-08/31/22)This positron emission tomography (PET) project examines the longitudinal relationship between the clearance of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) using a novel PET agent [11C]-butanol in association with brain amyloid.
Understanding the relationship between the brain’s connectivity networks and cognition in pre- and post-menopausal MS patients
Award or grant: Cornell University MRI Facility pilot grantMultiple sclerosis (MS) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory diseases wherein the body attacks protective tissue surrounding nerves. Women are more likely to develop MS compared to men with a female-to-male ratio of 2.8 to 1. The effect of the hormonal changes, in particular estrogen, on disease progression and annual relapse...
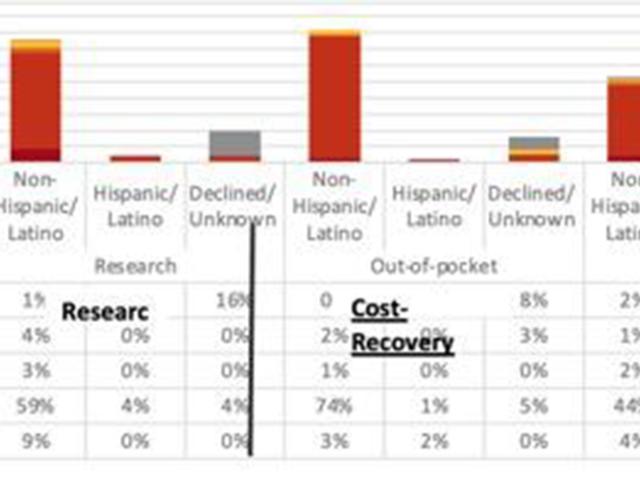
Effects of health economics on healthcare disparities
Addressing healthcare disparities that can be created with an uneven socioeconomic distribution of diagnostic tests and therapeutics. Here are a few examples from work we have produced through this initiative:A network-wide review of patients with access to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) Imaging and Therapy demonstrated that non-hispanic Whites were more likely to obtain PSMA positron...
Imaging biomarkers for disease severity and therapeutic response in CLN2 disease
Award or Grant: U54NS065768, BioMarin Pharmaceutical, 190-201, 190-202, 190-203Ceroid lipofuscionosis type 2 (CLN2) disease is a rare, rapidly progressing lysosomal storage disease with severe neurological complications including widespread neurodegeneration. The disease’s rarity, as well as the possibility of non-uniform progression depending on genotype, means that limited data are available...
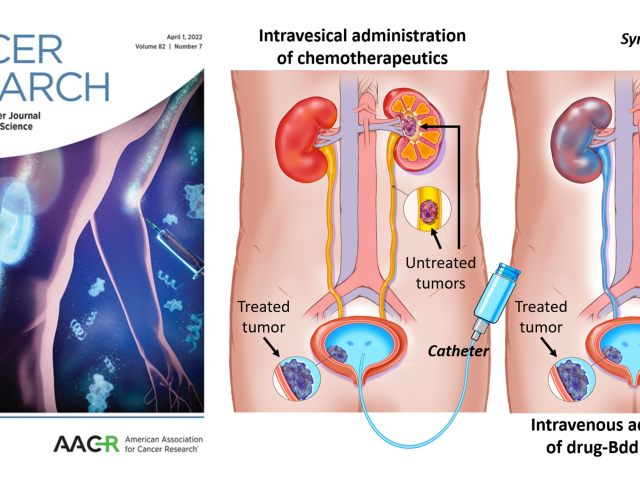
Urinary drug disposing system for treatments of kidney and bladder cancers
Most bladder cancer (BC) patients are diagnosed at an early stage. The standard treatment involves surgically removing tumors, followed by intravesical immunotherapy (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) or chemotherapy (ITC) to eradicate any residual cancer cells. However, current ITC methods are limited, with incomplete treatment, poor patient compliance, and a high recurrence rate. Furthermore,...
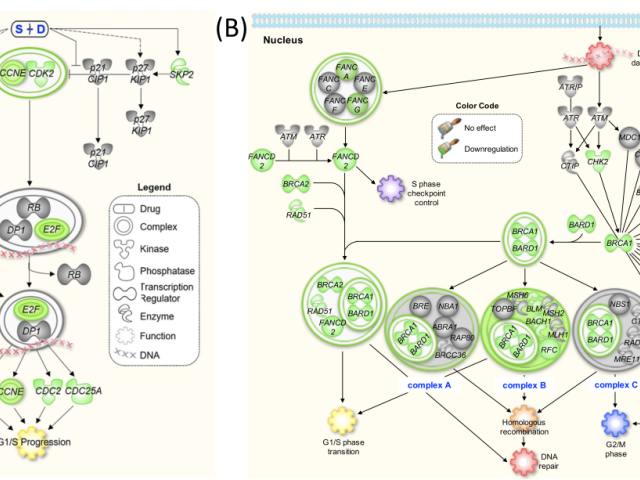
Mechanisms of anticancer agents
To improve the treatment outcome, multiple drugs of distinctive mechanism but complementary anticancer activities are often used to enhance the antitumor efficacy and minimize the risk of acquiring drug resistance. Specifically, we investigate the synergistic effects of drug combinations, with the aim of developing new therapeutic strategies, such as drug-induced targeting approaches (Fig. 6,...
Novel dynamic liver imaging method with flexible temporal and spatial resolution
Liver cancer is an increasing burden on public health. Currently, a 3D multi-phase contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exam is used to separate the arterial from the venous blood supply to any lesion to determine whether it is malignant or not. It relies heavily on the ability of the patient to sustain a breath-hold, but in a considerable subset of patients, this ability is...
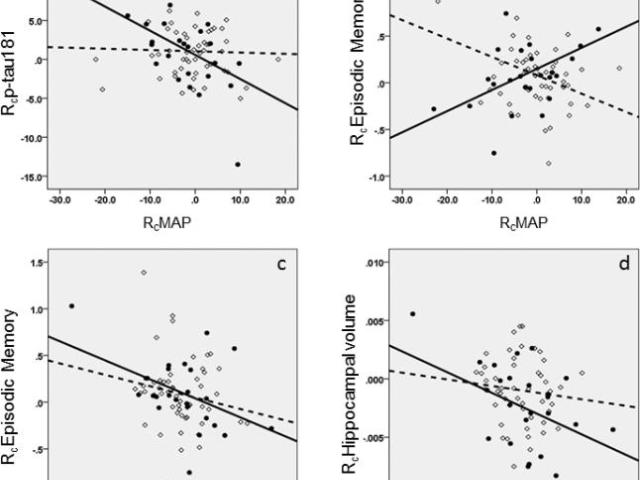
Blood pressure decrease correlates with tau pathology and memory decline in hypertensive elderly
In hypertension, cerebral blood flow (CBF) regulation limits are changed, and the threshold for blood pressure (BP) at which perfusion is safely maintained is higher. This shift may increase the brain's vulnerability to lower blood pressure in subjects with vascular disease. We found that, in hypertensive subjects over 60, but not in their normotensive peers, a longitudinal decrease in mean...
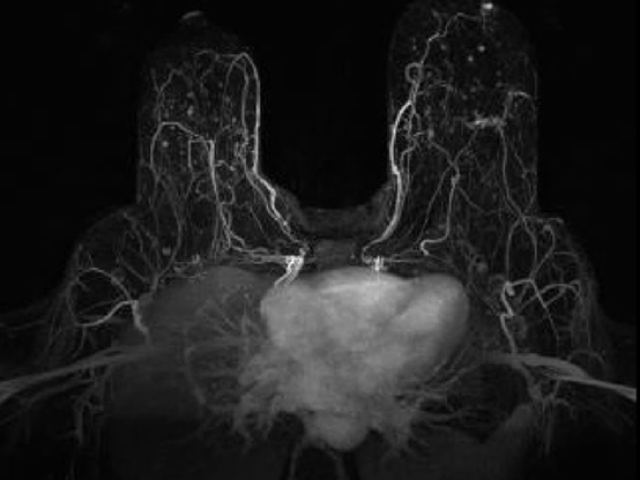
Active contrast encoding (ACE)-MRI study of breast cancer
Awards or Grants: R01 CA160620, National Cancer Institute (NCI), 2/1/2019-1/31/2024Description: Assessment of cancer treatment requires an effective non-invasive method of measuring both the vascular and cellular changes induced by therapies. The Kim team’s underlying hypothesis is that a single dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurement, using the active...
MRSaiFE: Real-time prediction of tissue heating in MRI
A crucial safety concern for ultra-high field (UHF) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the significant radiofrequency (RF) power deposition in the body in the form of local specific absorption rate (SAR) hotspots, leading to dangerous tissue heating/damage. This work is a proof-of-concept demonstration of artificial intelligence (AI) based real-time MRI safety prediction software (MRSaiFE)...