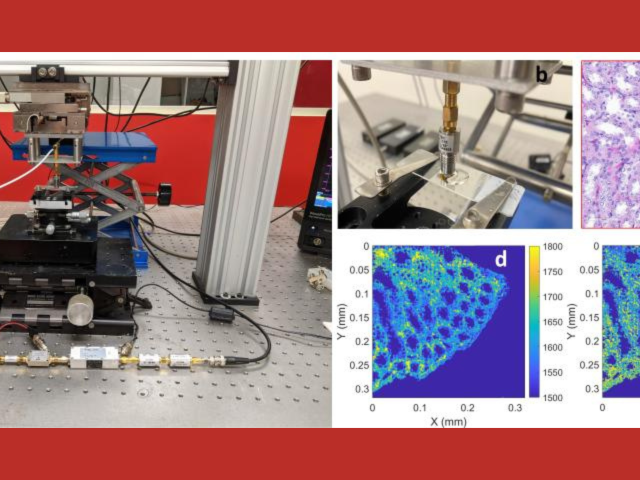
Next Generation Quantitative Acoustic Microscopy for Biomedical Application
The goal of this project is to develop the next generation of quantitative acoustic microscopy (QAM) systems. Specifically, data-science and coded-excitation approaches are applied for the first time to QAM technology to yield better image quality, decreased scanning time, and greater ease of use and to pave the way for a new generation of novel, low-cost, user-friendly QAM instruments. QAM...
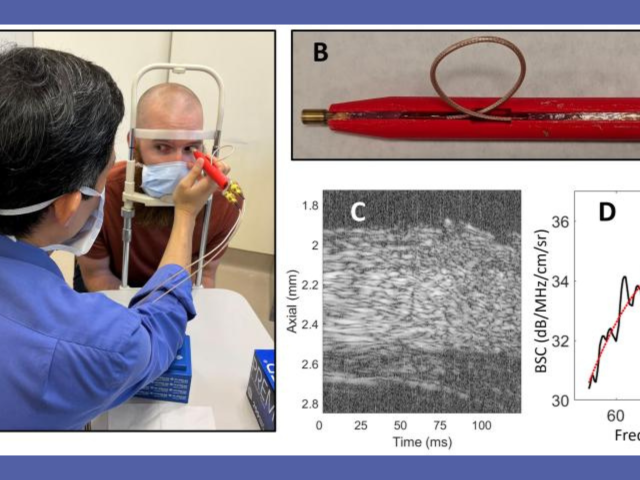
Novel in-vivo ultrasound-based point-of-care instrument to assess myopia level and progression
The goal of this project is to develop a novel, low-cost, compact, point-of-care (POC) ultrasound system to assess myopia severity and progression in vivo. Myopia prevalence is increasing worldwide and pathologic myopia is one of the leading causes of blindness. Myopia originates from structural and mechanical changes in the sclera that precede vision-threatening ocular changes. Currently, no...
Novel Quantitative Ultrasound methods for in-vivo histomorphology to grade early cartilage degeneration
The overall goal of this proposed research is to develop and test new ultrasound backscattering models for future quantitative-ultrasound (QUS) -based in-vivo screening and monitoring of early osteoarthritis (EOA). Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease that degenerates articular cartilage (AC) and is the most prevalent joint disease in the United States, causing more than $60 billion in...
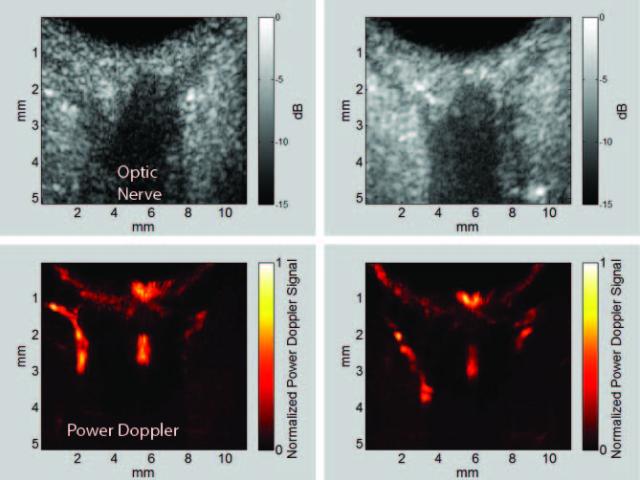
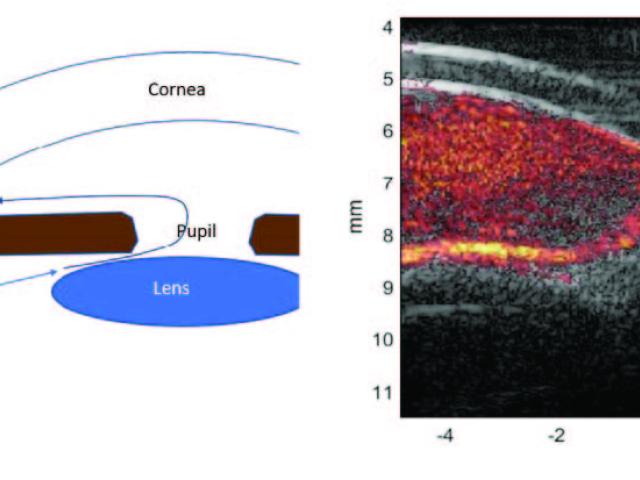
Ultrasound Perfusion Imaging in Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy and the leading cause of blindness, affecting over 3 million people in the United States. Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a well-known risk factor for this disease, but reduced ocular perfusion is also now appreciated to be an important risk factor in primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), the most common form of glaucoma. While optical methods such as optical...
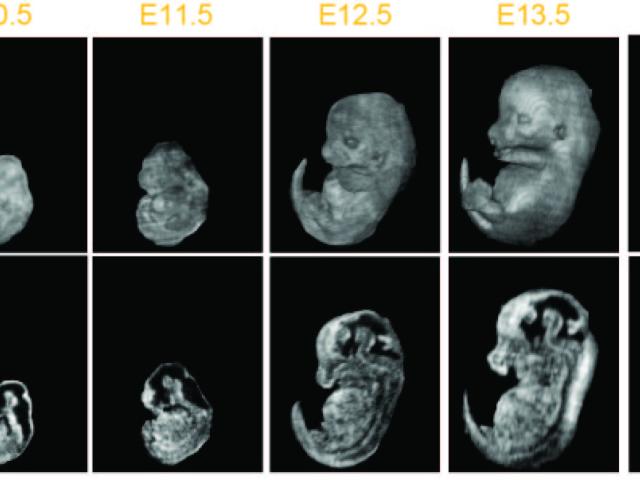
In utero mouse embryo phenotyping with high-frequency ultrasound
The goal of this proposal: phenotype early- to mid-gestational mouse embryos by segmenting select organ systems in 3D data sets acquired in utero with high-frequency ultrasound (HFU). The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC), which includes the NIH Knockout (KO) Mouse Phenotyping Program (KOMP2), will generate 20,000 mouse strains in the next decade, including many important models...
Ocular hemodynamics in rat model of glaucoma
Glaucoma is one of the primary causes of irreversible vision loss in this country and worldwide. It is a multi-factorial disease, or family of diseases, characterized by death of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and optic neuropathy. It has long been known that age, elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), and family history are glaucoma risk factors. It is now appreciated that reduced ocular perfusion...
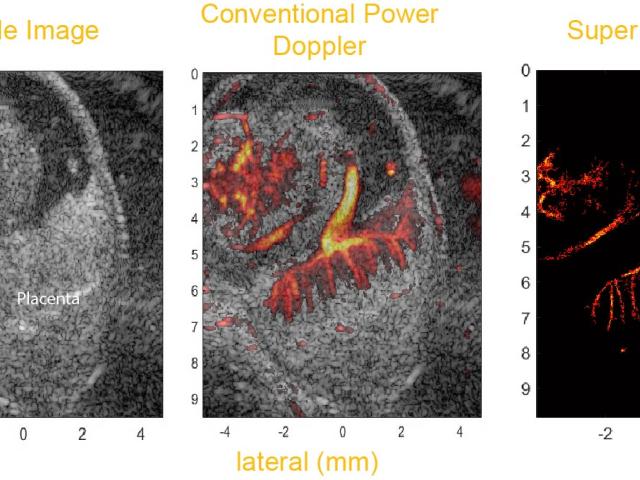
Fine-resolution mapping of micro vasculature after placental transport of acoustic nanodrops
A fundamental question in developmental biology is how specific molecules and genetic pathways control morphogenesis during embryonic development. Recent studies have shown that many of the same molecules and genetic pathways affecting organogenesis are involved in vascular development and patterning during angiogenesis. A major challenge is to develop rapid, in vivo mouse-embryo imaging methods...
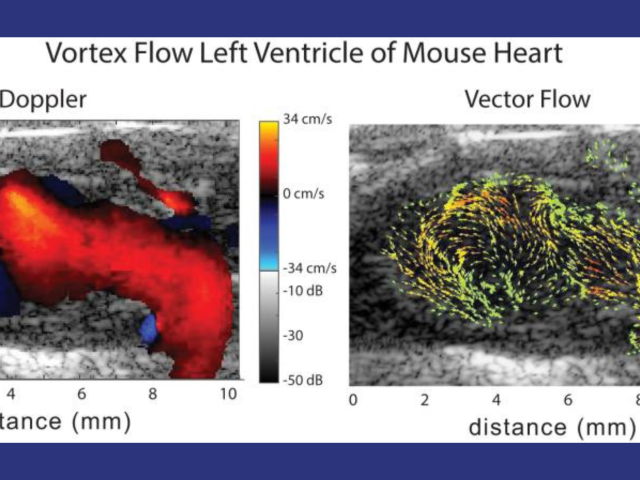
Murine cardiac vector-flow imaging with high-frequency 2D row-column CMUT arrays
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) accounts for one of every three deaths each year in the U.S. A substantial proportion of patients with CVD develop myocardial dysfunction. Imaging tools that permit early detection of abnormal hemodynamics and/or mechanics provide an opportunity to initiate targeted therapeutics and diminish the burden of disease. Mice are the most common model organism for...
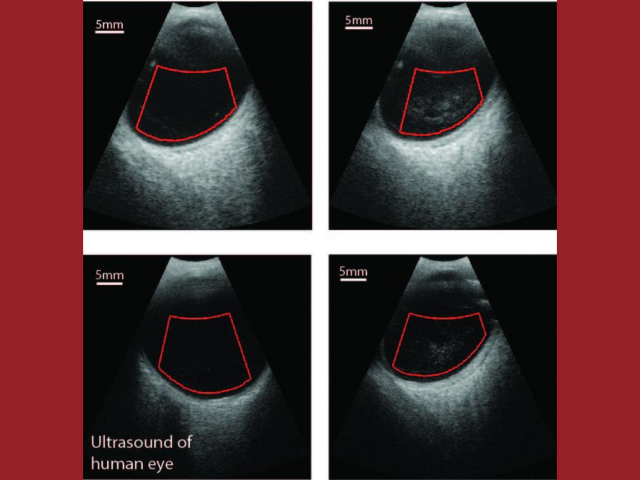
Vitreo-retinal disease imaging with 3D annular-array ultrasound
The goal of this translational project is to add quantitative ultrasound (QUS) capabilities to a clinical ophthalmic ultrasound system to characterize vitreous inhomogeneity (i.e., clinically significant vitreous floaters referred to as Vision Degrading Myodesopsia) as it relates to states of health and disease. Age-related changes due to collagen cross-linking and aggregation with liquefaction...
Quantitative MRI-based cerebral oxygen metabolism in Alzheimer's disease
Project Summary Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. Current clinical standard-of-care for assessing metabolic dysfunction in AD is 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET), based on a temporoparietal pattern of hypometabolism. However, 1) PET is impractical as a longitudinal assessment tool because it requires injection of a radioactive tracer, is...