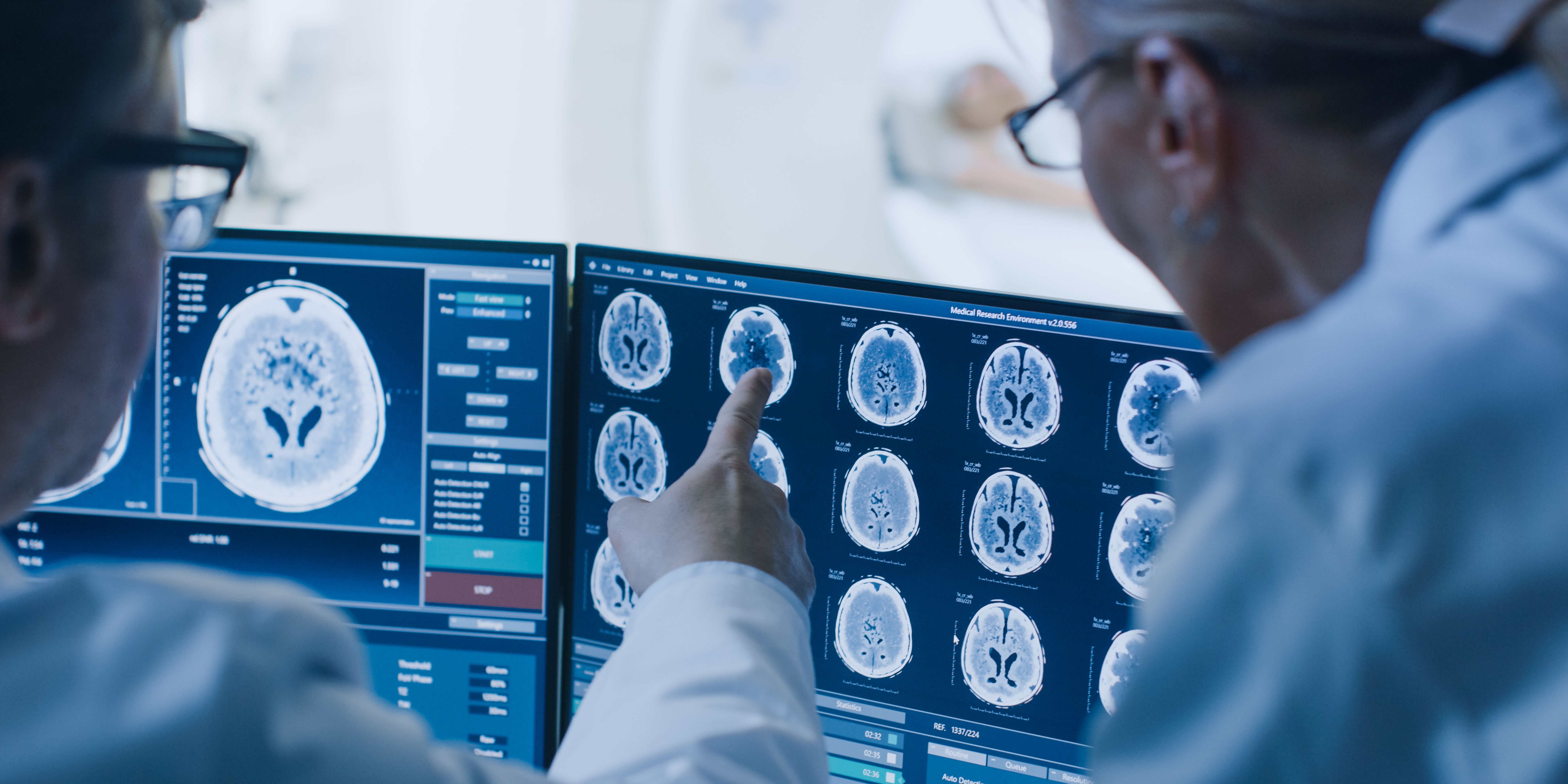
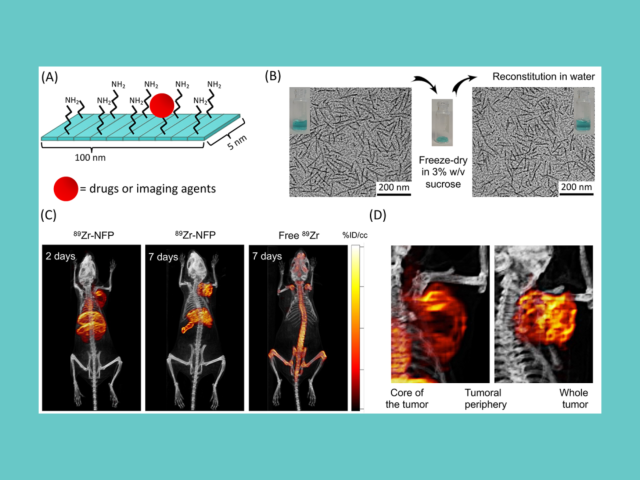
A multiplexed approach to improve tumoral targeting and chemotherapeutic treatment
Drawbacks of nanoparticles are: poor tissue extravasation, incomplete drug release, and off-targeted delivery to the reticuloendothelial system and organs. The Law lab developed a new nanofiber platform (NFP) displaying a unique dimension (0.5 x 5 x 100 nm) different from other nanoparticles. The NFP has an excellent tumor-targeting property (see film below). It can structurally transform into 10...
A multiplexed approach to improve tumoral targeting and chemotherapeutic treatment
Drawbacks of nanoparticles are poor tissue extravasation, incomplete drug release, and off-targeted delivery to the reticuloendothelial system and organs. The Law lab developed a new nanofiber platform (NFP) displaying a unique dimension (0.5 x 5 x 100 nm) different from other nanoparticles. The NFP has an excellent tumor-targeting property. It can structurally transform into 10-times larger...
Urinary drug disposing system
Most bladder cancer (BC) patients are diagnosed early. The standard treatment is to surgically remove the tumors, followed by intravesical immunotherapy (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) or intravesical chemotherapy (ITC) to eradicate any residual cancer cells. The current ITC are limited due to incomplete treatment, poor patient compliance, and high recurrence rate. In addition, clinicians are...
Anticancer agents
To improve treatment outcomes, multiple drugs of distinctive mechanisms but complementary anticancer activities are often used to enhance antitumor efficacy and minimize the risk of acquiring drug resistance. Specifically, the Law Lab investigates the synergistic effects of drug combinations to develop new therapeutic strategies, such as drug-induced targeting approaches, for cancer treatments....
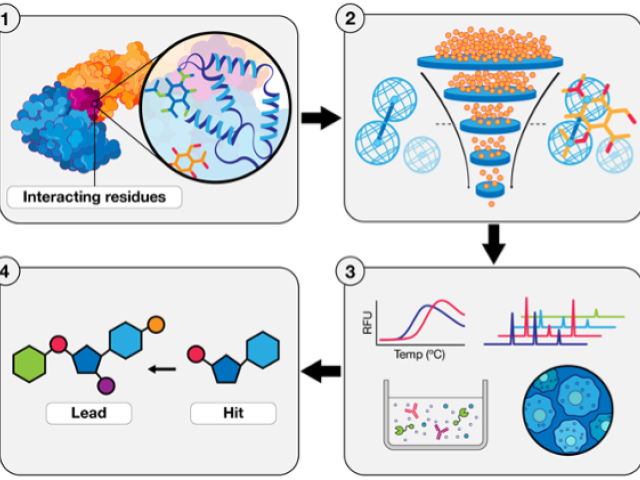
Therapeutic targeting of immune checkpoints with small molecules
Negative immune checkpoints are regulators of the human immune system that hinder the ability of T cells to attack cancer cells. There are currently no small molecules clinically approved as immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy. This project aims to validate new lead identification strategies to develop small molecules that can bind immune checkpoints and/or hinder the...
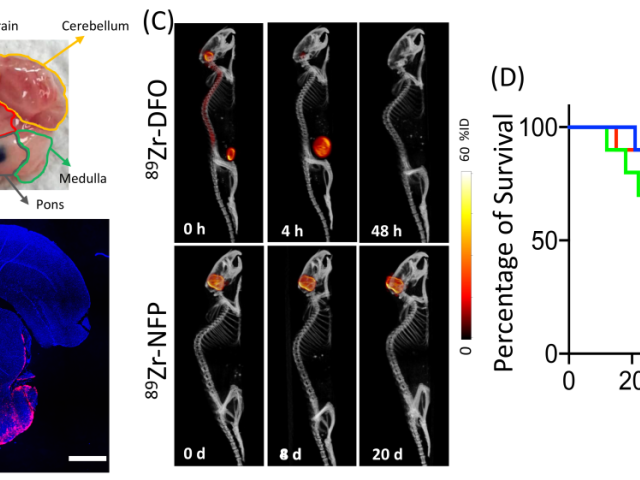
Multifunctional nanofiber for convection-enhanced delivery of theranostics to diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
Of all pediatric cancers, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is the most aggressive. Focal radiotherapy only prolongs patient survival for a few months. Chemotherapy does not improve patient survival as DIPG is intrinsically resistant to most chemotherapeutics. Furthermore, our brains naturally prevent most drugs from reaching the brain tumor. Convection-enhanced delivery (CED), is a direct...
WCM catchment Prostate Cancer Health Impact Program (pCHIP)
Dean’s Health Disparity Research Award WinnerProstate cancer (PCa) is the second leading cause of cancer death in American men. Several studies have shown higher mortality rates among African American and Hispanic men relative to White men. Lower screening rates in ethnic minorities, along with poor access to treatment resources, medical information, high quality of care, new imaging modalities,...
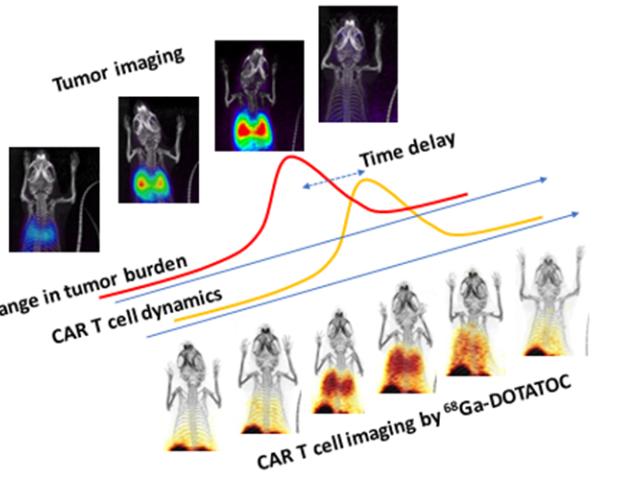
Developing CAR T cells for cancer therapy
The lab is developing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells against new tumor antigens; novel CAR constructs for simultaneous therapy and imaging; and various ways to augment the potency of CAR T therapy against solid cancers. The lab’s recent successes include: demonstration of somatostatin receptor-2 (SSTR2) for imaging T cell distribution and activity in vivo (using positron emission...
New formats of antibodies for imaging and bispecific recognition
Antibodies are an important class of biologic drugs in oncology and inflammatory disease settings, either in native forms or in modified forms, to carry small molecules or to recognize more than one antigen. Antibodies can also be modified to become molecular diagnosis agents for real-time imaging of diseased cells and tissues in the body. The Jin lab uses in vitro techniques such as phage and...
Nanoparticles for molecular imaging and hyperthermia
Two major hurdles in cancer therapy are early detection of tumors in the body, and efficient delivery of drugs to tumor cell targets. Contrast agents modified to recognize unique and over-expressed markers on the tumor cell surface show great potential in cancer diagnostics. The delivery platform is built on liposomes, polymers, and magnetic nanoparticles with their surface modified for the...