Pre-processing of fMRI data
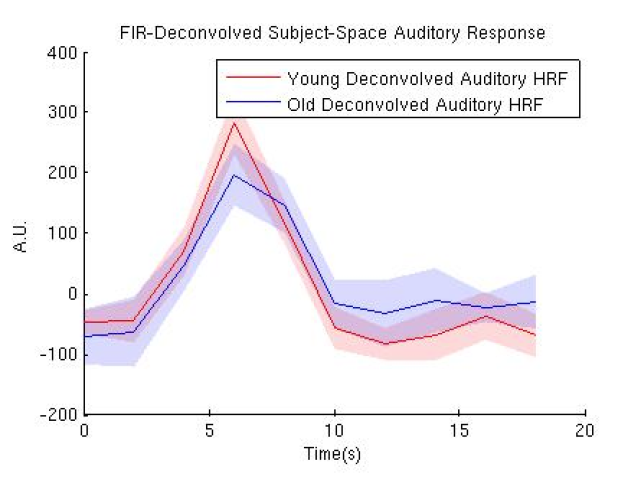
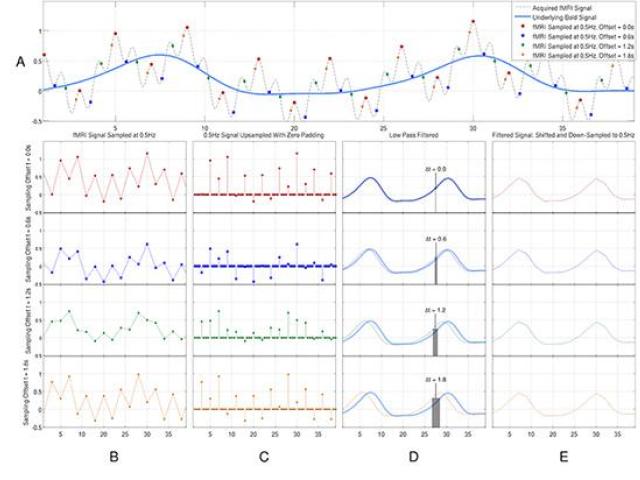
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute on Aging (NIA) 5R01AG026158Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) pre-processing requires urgent attention, particularly given the increasingly complex derivation of functional connectivity-based biomarkers in resting-state fMRI. High scanner and thermal noise, irregular sampling in interleaved slice acquisition,...
Optimal recovery of BOLD signal from interleaved fMRI data
The QNL has developed an optimal technique to extract the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal from interleaved functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. In this project, the lab uses a well-established, simple signal reconstruction method to correct irregular sampling problems in interleaved slice acquisition. The lab has shown the superiority of this optimal method, particularly...
Region-based spatial normalization
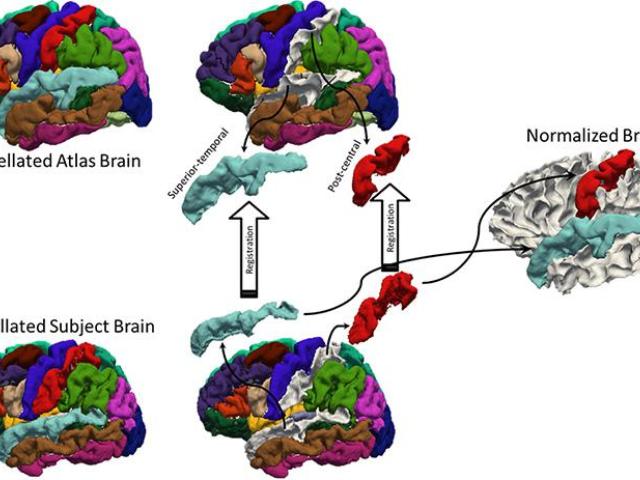
In functional neuroimaging studies of cognitive aging, age-related changes in brain morphology make it difficult to co-register brains, which is a key step for studies comparing task-related activation in young and old groups. To demonstrate the problem’s severity, the video below shows 29 participants’ brains after spatial normalization; corresponding regions are shown in the same color, and the...
Multilateral Markov random field and brain subcortical segmentation
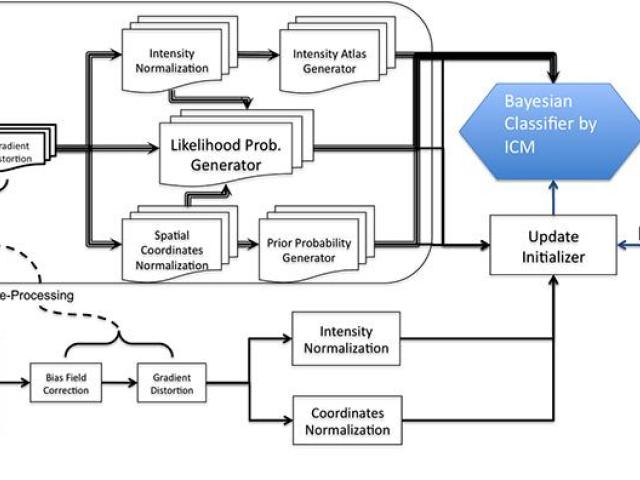
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging (NIH/NIA) 5R01AG055299, NIH/NIA 5R01AG055422, NIH/NIA 5 R01 AG057681Conventional Markov random field (MRF) is hampered by noncausality, and its causal definitions lead to difficulties. For instance, the Markov mesh random field has strong diagonal dependency in its local neighboring system. The Quantitative Neuroimaging...
“Spray-and-See” tumor highlighter for surgical guidance
Cancerous tissue surgical resection is a critical procedure for solid tumor treatment. During the operation, the surgeon primarily identifies the cancerous tissues by naked-eye visualization under white light; therefore, the outcome heavily relies on the surgeon’s experience. CypH-11, a near-infrared pH-responsive fluorogenic dye, was developed to delineate the tumor margin in real-time for...
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for the study of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Award or Grant: The Leon Levy FoundationIn this research project, the Kovanlikaya lab used advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), arterial spin labeling (ASL), phase contrast cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow measurement and structural volumetric MRI to develop quantitative criteria to diagnose normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) patients more...
BHII Clinical Core Operations Co-Director Silky Pahlajani, M.D., talks about Alzheimer’s disease
Dr. Silky Pahlajani discusses Alzheimer's disease: the definition, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnostic/confirmation testing, and who can be affected. Learn what is known about prevention, how the condition is currently treated, and what future treatments might become available.
BHII Neuropsychiatrist Silky Pahlajani, M.D., talks about autoimmune disease
Dr. Silky Pahlajani is an Assistant Professor of Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychiatry in the department of neurology at Weill Cornell. She is also an Assistant Attending at New-York Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. She has training in autoimmune/neuroinflammatory brain disorders including autoimmune encephalitis. Dr. Pahlajani was a speaker for the April 2019 AE Symposium...
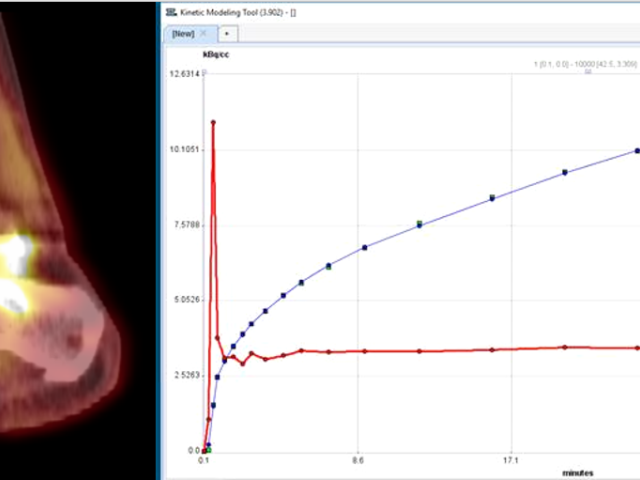
Measurement of bone blood flow and osteoblastic turnover using MRI and PET
Bone blood flow (BBF) and turnover may be altered in many disease states such as osteoarthritis (OA), bone marrow lesions, and trauma or fracture. Dr. Dyke’s group pioneered the use of pharmacokinetic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) modeling of various agents to measure BBF and turnover in disease progression of OA, and following injury. These techniques...
Compact representations of dynamic liver MRI
Award or Grant: R01 CA181566-01A, National Institutes of Health (NIH)The goal of the proposed research is to develop a sensitive and early measurement of treatment response in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent malignant liver cancer. Relevance: This research will result in a quantitative measure of the malignancy of liver cancer, whose burden on the public health is expected to...