Soft robotic sensor arrays for semiautomated intubation procedures
Intubation Procedures: For patients with obstructed airways or difficulty breathing, intubation is a lifesaver. Roughly 50 million intubation procedures are performed each year. In this procedure, a physician or emergency medical service (EMS) worker guides an endotracheal tube down the airway of the patient to maintain the ability to breathe. Especially for patients with obstructions or...
Quantitative MRI of lesion iron and myelin repair
Award or Grant: National MS Society RR-1602-07671The Nguyen Lab’s objective is to establish the association between lesion iron and subsequent myelin recovery in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. The lab will develop quantitative and reliable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods including myelin water fraction (MWF) mapping and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) to measure iron and...
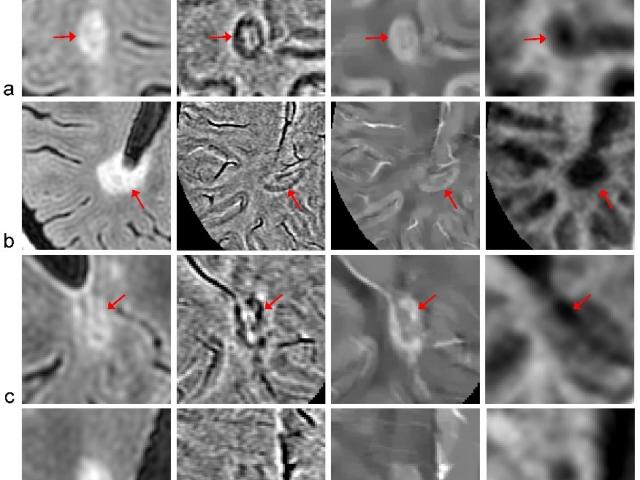
Quantitative susceptibility mapping of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage
Award or Grant: R21 NS116516; R01 NS123576-01A1 (not yet funded)The team’s key objective is to use quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) to establish reliable, noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for identification and risk stratification of unstable carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Currently, decisions about carotid revascularization to prevent stroke, such as carotid endarterectomy...
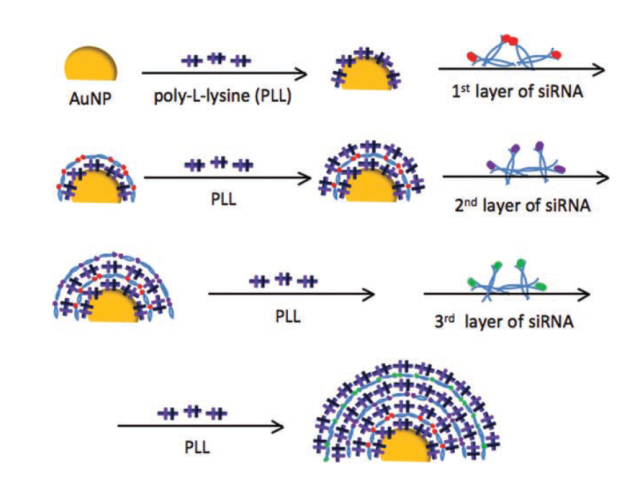
Effective gene silencing by multilayered siRNA-coated gold nanoparticles
More than a decade ago, to improve cell tracking efficiency, Dr. Seung Koo Lee, in the lab of Dr. Ching Tung, formulated a layer-by-layer nanoplatform. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) had been proposed to treat various diseases by silencing genes, but delivery was problematic. A carefully built assembly approach was generated and used to prepare a protease-assisted nano-delivery system. Protease-...
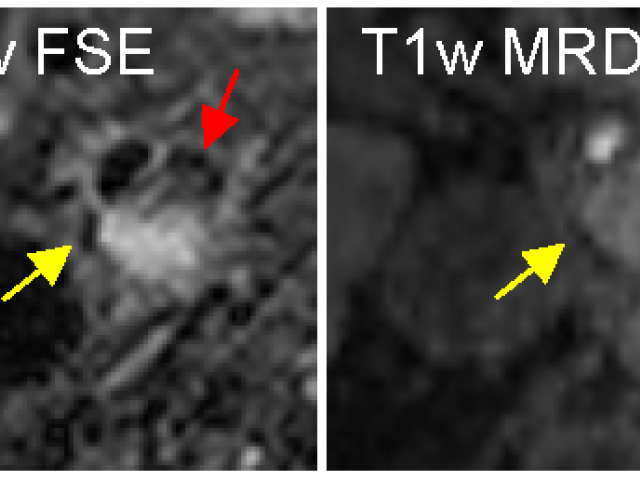
No-Gd MRI for monitoring disease status in multiple sclerosis
Our patients objective is to eliminate gadolinium (Gd) injections in routine follow-up magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of multiple sclerosis (MS) using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a direct response to calls issued by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to re-evaluate repetitive Gd administration to patients. We have pioneered QSM...
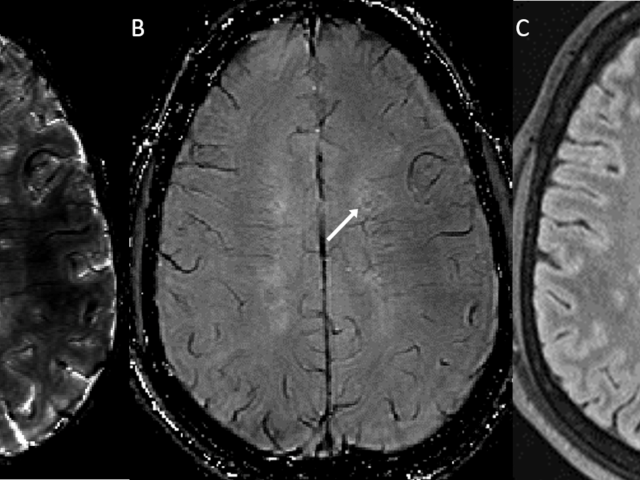
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a non-invasive imaging biomarker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease
The long-term objective of the Wang lab’s research is to establish quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) marker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The lab’s scientific premise is that QSM can measure iron overload involved in AD progression. The lab’s approach is to establish QSM as an MRI marker for predicting...
7T magnetic resonance imaging system for basic, translational and clinical research
Weill Medical Medicine (WCM) of Cornell University has requested High-End Instrumentation Grant Program support to purchase a state-of-the-art human whole-body seven tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system as a Special Use Instrument (SUI; PAR-19-177). This 7T MRI is part of a major WCM strategic investment in crucial imaging infrastructure needed to advance basic, translational and...
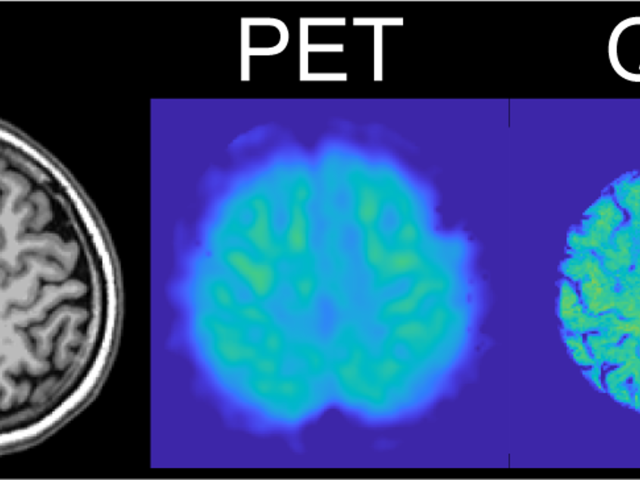
Feasibility of challenge-free QSM based quantitative mapping of cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen
The objective of this proposed research is to develop a noninvasive, easily accessible and widely usable imaging method to map the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (CMRO2). Oxidative metabolism is the main source of energy for proper human brain function. Consequently, brain tissue is highly susceptible to damage associated with oxygen deficiency, including hypoxia in Alzheimer’s...
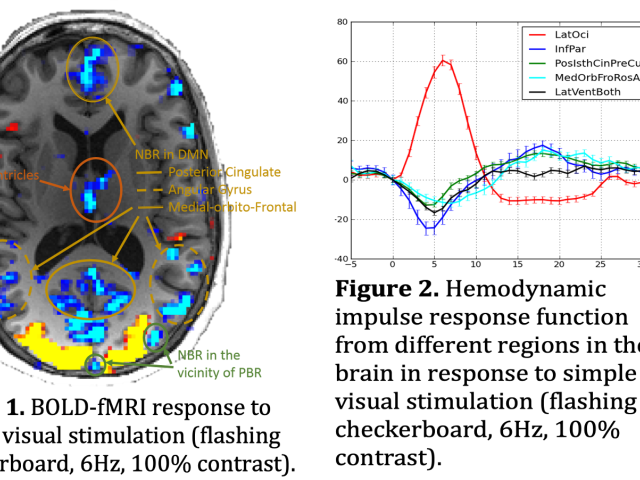
Negative bold response
The Quantitative Neuroimaging Laboratory’s (QNL’s) main research project is investigating the neural and neurophysiological mechanisms underpinning the negative blood-oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) response (NBR). Emerging evidence sheds light on the mechanism underlying the task-based positive BOLD response; however, the accompanying NBR is mostly unknown (Bentley et al.: 2016; Hayden et al...
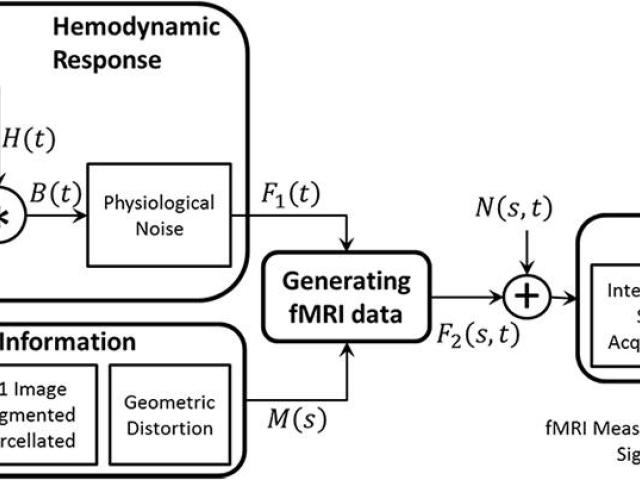
fMRI simulator
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute on Aging (NIA) 3RF1AG038465A comprehensive functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) simulator not only helps evaluate and improve the present blood oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) extraction methods for false-positive detection, but it is also the only available tool for evaluating false-negatives. The fMRI simulator...