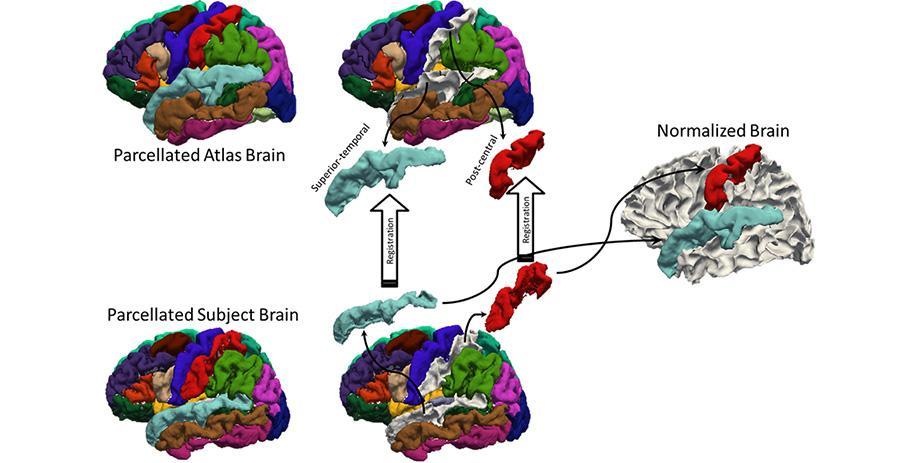
In functional neuroimaging studies of cognitive aging, age-related changes in brain morphology make it difficult to co-register brains, which is a key step for studies comparing task-related activation in young and old groups. To demonstrate the problem’s severity, the video below shows 29 participants’ brains after spatial normalization; corresponding regions are shown in the same color, and the magnitude of the variability for each voxel between subjects is clearly illustrated. To address this issue, we are developing a region-based spatial normalization (RBSN) technique that increases the functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data localization’s accuracy. While the prevailing spatial normalization method tries to align all human brain regions at once, RBSN aligns each of the brain’s neuroanatomical regions independently, thereby providing more accurate localization of activation, and ensuring that group analyses test the same brain area in each study participant. Additional statistical power is also provided by enhanced between-participant registration, detecting activation in regions that may not have reached the significance level using prevailing methods. (For example, it will reduce type II error). It may also rule out previously noted areas of activation that were detected for artifactual reasons. (For example, it will reduce type I error).
Related Publication
D.B. Parker, et al., “Optimal slice timing correction and its interaction with fMRI parameters and artifacts,” Med. Image Anal.: Aug. 2016.
D.B. Parker, et al., “Optimal signal recovery from interleaved FMRI data,” IEEE international Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: 2015, Brooklyn, New York.
Software Released
Version 1.3 is the most updated, robust package. It can be downloaded from github via the link below. The binaries for CentOs 6.5 are also available. Running the code with no input will print out the help—this should be self-sufficient for its execution. Please report any bugs to Dr. Razlighi for investigation.