Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging (NIH/NIA) 5R01AG055299, NIH/NIA 5R01AG055422, NIH/NIA 5 R01 AG057681
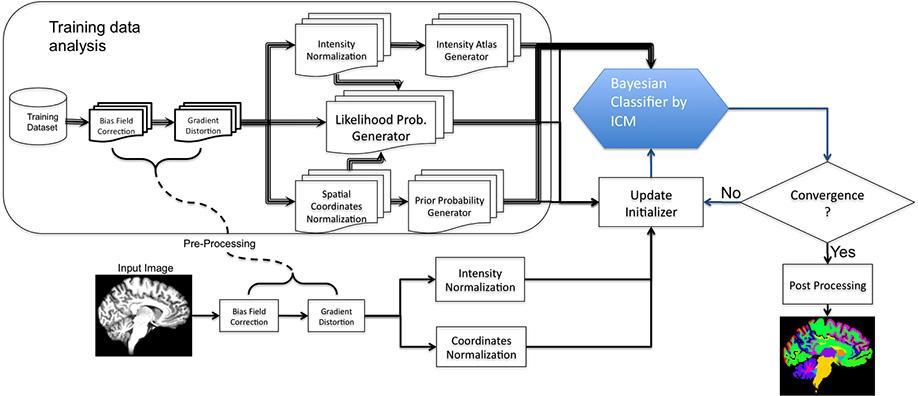
Conventional Markov random field (MRF) is hampered by noncausality, and its causal definitions lead to difficulties. For instance, the Markov mesh random field has strong diagonal dependency in its local neighboring system. The Quantitative Neuroimaging Laboratory (QNL) introduced multilateral Markov random field (MMRF) to overcome this issue. MMRF is an MRF—but not necessarily vice versa. Low-dimensional local distribution yields a causal MRF’s joint distribution; whereas, in conventional MRF, it is only given through Gibbs distribution. For homogenous fields, a joint histogram is used to estimate low-dimensional joint probability density functions (PDF)s, and for inhomogeneous fields, a few samples of the field are employed, making the model tied to the image in use. By using MMRF for image entropy and mutual information computation, the QNL has showed its superiority in brain image registration.
The lab has also developed a maximum a posteriori (MAP) Bayesian classifier—MMRF-MAP—to improve the segmentation accuracy in the brain’s subcortical structures. Compared to Freesurfer subcortical segmentation, the QNL’s technique showed an improvement in most regions. As the QNL extends the model to 3D random field, it is developing a 3D model classifier, which the lab believes will significantly increase the segmentation’s accuracy.
Related Publications:
Q. R. Razlighi, et al., Spatial Mutual Information as Similarity Measure for 3D Brain Image Registration, IEEE J. Transl. Eng.: 2014. vol.2, no., pp.27-34.
Q. R. Razlighi, et al., Evaluating Similarity Measures for Brain Image Registration, J. Vis. Communi. Image Represent.: 2013, vol. 24, no. 7, pp. 977-987.
S. Yousefi, N., et al., Bilateral Markov Mesh Random Field and its Application to Image Restoration, J. Vis. Commun.: 2012, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 1051-1059.
Q. R. Razlighi, et al., Causal MRF for Brain MR Image Segmentation, Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, San Diego: 2012 Aug..
Q. R. Razlighi, et al., Computation of image spatial entropy using quadrilateral Markov random field, IEEE Trans. Image Process.: 2009, vol. 18, no. 12, pp. 2629-39.
Software Released
Please contact Dr. Razlighi for the Python code and instruction.