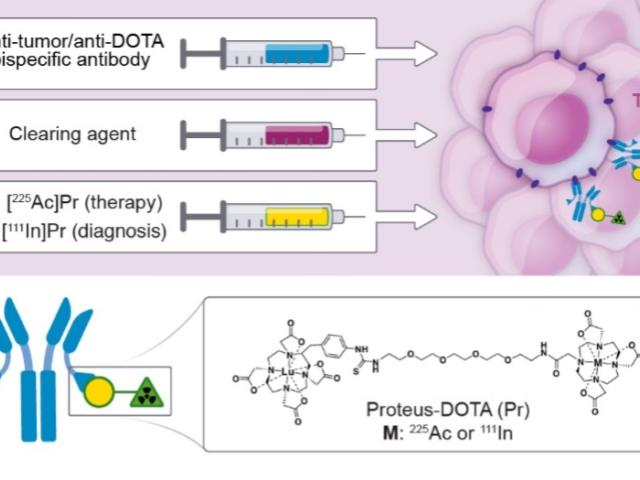
Alpha radioimmunotherapy using 225Ac-proteus-DOTA for solid tumors - safety at curative doses
We developed the α-emitter DOTA-ligand bound radionucleuide-based pre-targeted radioimmunotherapy (DOTA-PRIT) with 225Ac and the requisite companion biomarkers (111In, 89Zr). Please see Theranostics: 2020, 10(25):11359-11375 and Nucl. Med. and Biol.: 2021, 96: p. S3-S4.
The effects of iron on oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s biomarkers in amyloid-positive and negative elderly individuals
Award or Grant: R01, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute on Aging (NIA) (2020-2025)Preclinical and postmortem studies have shown that iron colocalizes with beta-amyloid plaques, and iron dyshomeostasis can lead to free radical formation and neuronal loss. Using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), and fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s...
Novel algorithms for reducing radiation dose of CT perfusion
Award or Grant: R44, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) (2017-2022)This study will optimize and validate a k-space weighted image average algorithm for reducing dose of computed tomography (CT) perfusion images.
Predictive model of spread of Parkinson's pathology using network diffusion
Award or Grant: R01, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) (2016-2021)This study will aim to use brain connectivity to quantitatively model the spread of Parkinson’s disease pathology using a novel “network diffusion” model, based on in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of patients.
Effects of traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder on Alzheimer’s disease in veterans using the Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI-DoD)
Award or Grant: Department of Defense (2013-2018)The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative of the Department of Defense (ADNI-DoD) was a multicenter, observational study to determine the effects of traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSD) in veterans on subsequent development of brain amyloidosis and Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Effects of Type 2 diabetes and glycemic control on brain amyloid deposition in nondemented adults
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) (2013-2015)This study investigated the relationships between (1) insulin resistance and brain amyloidosis and, (2) oxidative stress and brain amyloidosis in nondemented individuals, using magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy and amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) scans with...
Multimodal imaging of apolipoprotein E epsilon 2 carriers
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) Clinician-Scientist T32 Training Grant in Biomedical Imaging (2009-2010)This study used multimodal imaging techniques (voxel-based morphology, arterial spin labeling perfusion, and diffusion tensor imaging) to characterize the effects of the APOE e2 allele on the brain. The APOE...
Novel nanomedicines for diagnosis and therapy
By hitting multiple action mechanisms, combination therapy efficiently tackles cancer; however, drugs administered, simultaneously or sequentially, may not reach the targeted sites with the desired dose and ratio. The Tung lab develops various strategies to improve delivery efficiency and integrated therapeutic benefit; these strategies have been applied to multidrug combination therapy, self-...
Impact of high LET radiation on host immune response to augment immunotherapy
Award or Grant: SPORE in Prostate Cancer Developmental Research Program Award Local radiotherapy has been recognized as a powerful inducer of acute inflammation and immunogenic cell death. Seminal work implicating T cells in the response to local radiotherapy (RT) was reported years ago. But it was only recently that mechanisms conveying immunogenicity of irradiated tumor cells have been...
DOTA-based pre-targeting of alpha emitters
Antibody-based targeting provides superior specificity for radionuclide therapy. However, it suffers from low absorbed dose compared to external beam radiotherapy and normal tissue toxicity due to the slow circulation and tumor uptake of antibodies. Pre-targeted radioimmunotherapy separates the slow antibody targeting phase from rapid delivery of the radionuclide by small anti-chelate ligands....