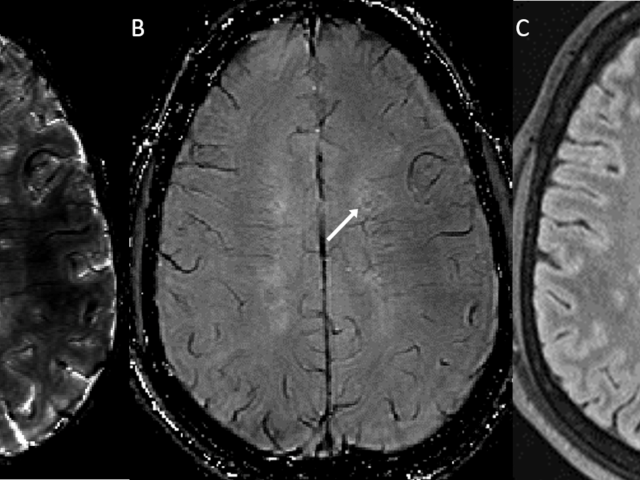
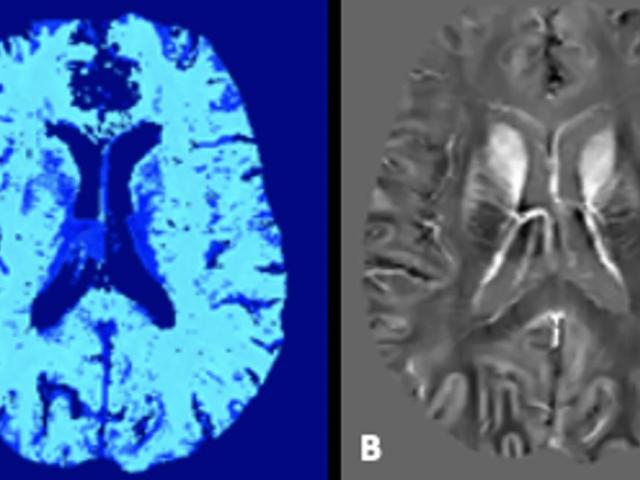
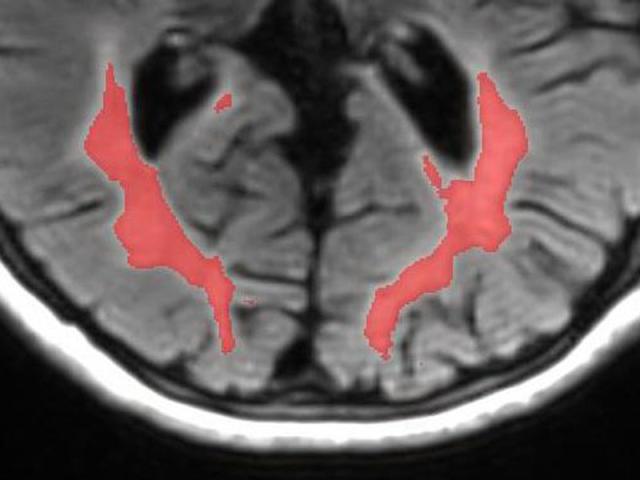
Quantitative mapping of brain tissue free water in preclinical AD
This project develops a new biomarker of glymphatic clearance by mapping brain tissue free water. We hypothesize that the increased brain parenchyma cerebrospinal fluid fraction (CSFF) is predictive of ventricular CSF clearance, future amyloid and tau lesions and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
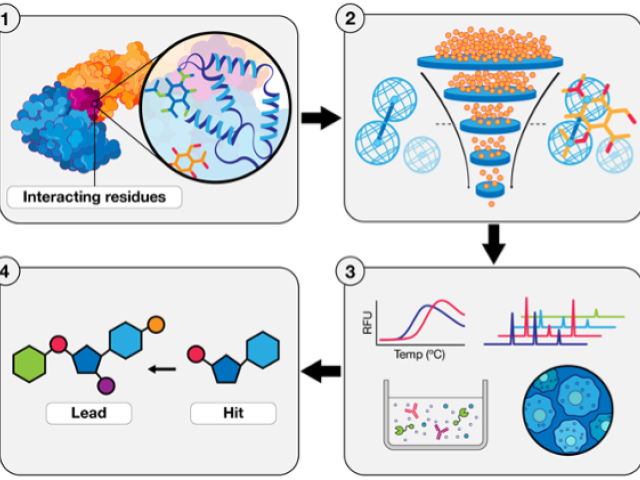
Therapeutic targeting of immune checkpoints with small molecules
Negative immune checkpoints are regulators of the human immune system that hinder the ability of T cells to attack cancer cells. There are currently no small molecules clinically approved as immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy. This project aims to validate new lead identification strategies to develop small molecules that can bind immune checkpoints and/or hinder the...
Acute genetic manipulation of phosphoinositide metabolism to rescue lipid and behavioral deficits in AD mouse model
Using optogenetics to temporally and spatially regulate phosphoinositide lipid synthesis in the mouse brain, the McIntire lab has shown amelioration of phosphoinositide dysregulation and behavioral benefit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Screening for phosphoinositide-modifying enzymes that prevent amyloid-induced synaptic loss in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived neurons
Screening for phosphoinositide-modifying enzymes that can prevent amyloid-induced synaptic loss in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived neurons.
Multiple sclerosis lesion magnetic susceptibility activity
The long-term objective of this project is to improve the ability to monitor inflammatory and neurodegenerative processes in multiple sclerosis (MS) for effective diagnosis and treatment. The specific goal: to establish the time course of magnetic susceptibility of lesions as a sensitive probe of demyelination and iron content associated with inflammatory processes. Currently, gadolinium...
Quantitative susceptibility mapping as a non-invasive imaging biomarker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease
This study will establish cellular sources of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) signal in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain tissue, and establish QSM as a predictor of neurodegeneration, using structural and metabolic magnetic resonance (MR) metrics.
No-Gd MRI for monitoring disease status in multiple sclerosis
This study will establish the diagnostic accuracy of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in monitoring disease in multiple sclerosis patients, without the use of intravenous gadolinium, and in predicting acuity of white matter lesions.
7T magnetic resonance imaging system for basic, translational and clinical research
This is a High-End Instrumentation Grant to provide support for a state-of-the-art human whole-body seven Tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system as a Special Use Instrument at WCM.
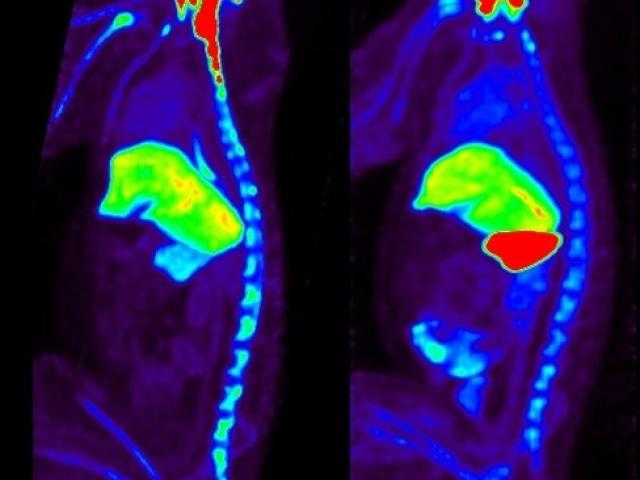
Rapid noninvasive whole-body imaging of AAV gene transfer vectors
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01) EB027918Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a widely used vector for gene delivery. Its in vivo distribution, though, has not been well characterized, as most studies are based on rodent biopsy or necropsy data. The distribution is also dependent on route of administration and pre-existing immunity. The goal of this project was to develop an...
Quantitative methods for preclinical Ac-225 imaging
Award or Grant: Radiology/Citigroup Biomedical Imaging Center Pilot AwardIt is well documented that molecularly targeted radiotherapy, such as pre-targeted radioimmunotherapy, can be optimized on a patient-specific basis with pre-therapeutic imaging and dosimetry. This can be carried out with theranostic isotopes such as the beta/gamma emitter lutetium (Lu)-177, or with therapeutic isotopes in...