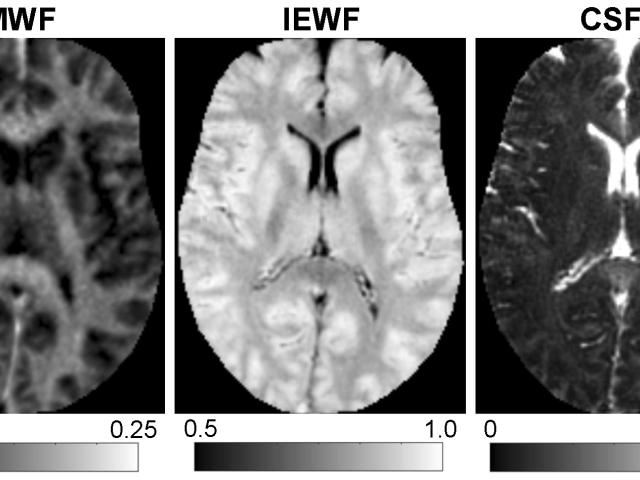
Quantitative mapping of parenchymal CSF fraction in Alzheimer’s disease
Award or Grant: R01 AG079326-01The team’s objective is to develop a new imaging method for quantitative mapping of parenchymal cerebrospinal fluid fraction (CSFF). The team’s preliminary data showed CSFF increased in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and was associated with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) bulk flow reduction and decreased ventricular CSF clearance. More importantly, increased CSFF correlated...
QSM to guide iron chelating therapy in transfusional iron overload
The overall objective of this research is to improve the safety of iron-chelating therapy (ICT) in patients with transfusional iron overload by developing accurate non-invasive measurement of the liver iron concentration (LIC), the best measure of the body iron burden in all forms of systemic iron overload. The lab’s scientific premise is that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), using quantitative...
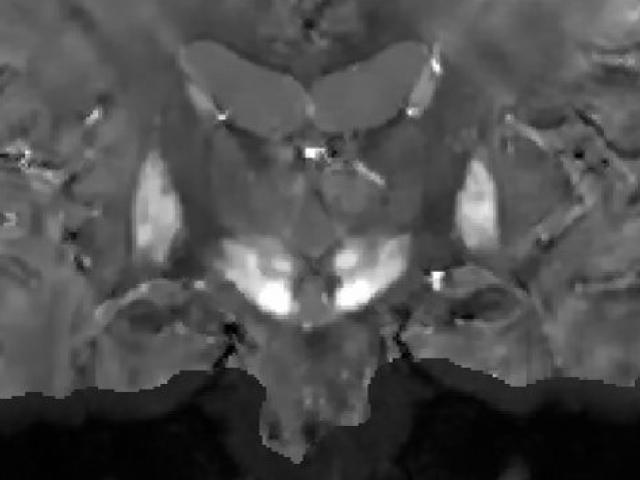
Quantitative mapping of substantia nigra iron in Parkinson’s disease
The long-term objective of this project is to develop noninvasive, robust, sensitive and accurate midbrain iron mapping for Parkinson's disease (PD). PD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dopaminergic neuron loss in the substantia nigra pars compactor (SNc) and consequent motor disorders. While the neurodegenerative processes in PD may be multifactorial, prooxidant iron elevation in...
Clinical summer immersion for biomedical engineering Ph.D. students
We propose a summer clinical immersion program at the Weill Medical College of Cornell University that brings Biomedical Engineering (BME) Ph.D. students from the Ithaca Engineering College Campus to the New York City Medical College Campus for dedicated intensive clinical exposure in the summer between their first and second year of graduate training. Each student will take bioethics lectures;...
MRI method for quantitatively mapping cerebral microbleeds
The objective of this research is to develop a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method for mapping iron deposits in cerebral microbleeds (CMB). There is significant scientific and clinical interest in studying CMB, which are focal lesions of hemosiderin deposits from red blood cells leaked out of small brain vessels. CMB have become an important concern for managing stroke patients,...
Gradient-echo spectroscopic imaging study of saturated fat and breast cancer
Award or Grant: R01CA219964, National Cancer Institute (NCI) (02/01/18 – 01/31/23). Description: The role of breast fatty acid composition in breast cancer development, in conjunction with breast density and body mass index, has not been fully investigated. The central hypothesis of the Kim lab is that its recently developed gradient-echo spectroscopic imaging method can be used to investigate...
Assessment of placental perfusion and oxygenation using ASL and QSM
In the management and treatment of pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction (FGR) and preeclampsia (PE) due to placental insufficiency, early and reliable detection is critical. For, once clinically evident, those pathological changes are irreversible. But there is no validated in-vivo method that can be routinely used in the clinic for non-invasive assessment of placental function. In...
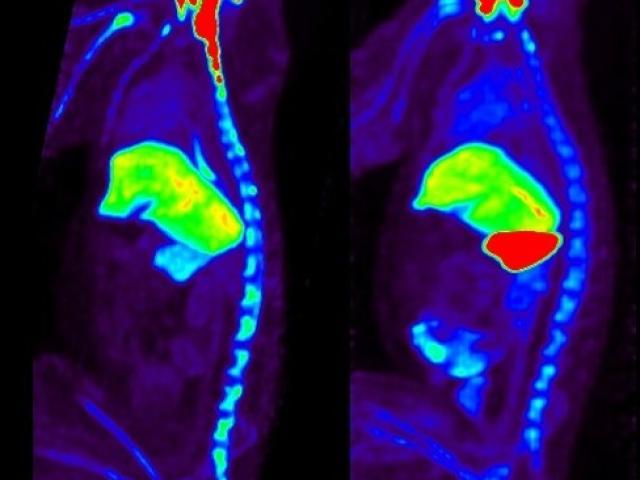
Rapid non-invasive whole-body imaging of gene transfer vectors
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH), R01 EB027918The goal of this project is to develop noninvasive, safe, temporal monitoring of adeno-associated viral vector (AAV) biodistribution following in vivo administration that can be ultimately used in humans. The lab’s strategy is to covalently radioiodinate AAV capsids using the positron emitting isotope iodine (I)-124, and to track...
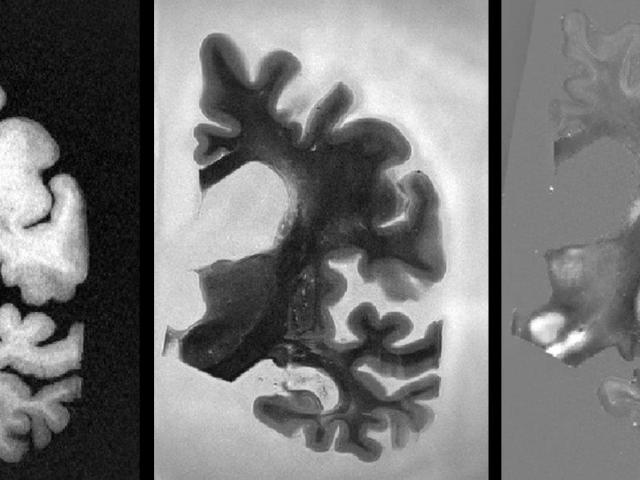
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a non-invasive imaging biomarker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease
A long-term objective of our research is to establish QSM as a noninvasive MRI marker for predicting neurodegeneration in AD. Our scientific premise is that QSM can measure iron overload involved in AD progression. We propose to establish QSM as an MRI marker for predicting neurodegeneration ex vivo using AD brain tissue pathology, and in vivo by correlating QSM with neurodegeneration measured...
Quantitative MRI-based cerebral oxygen metabolism in Alzheimer's disease
Project Summary Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia. Current clinical standard-of-care for assessing metabolic dysfunction in AD is 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET), based on a temporoparietal pattern of hypometabolism. However, 1) PET is impractical as a longitudinal assessment tool because it requires injection of a radioactive tracer, is...