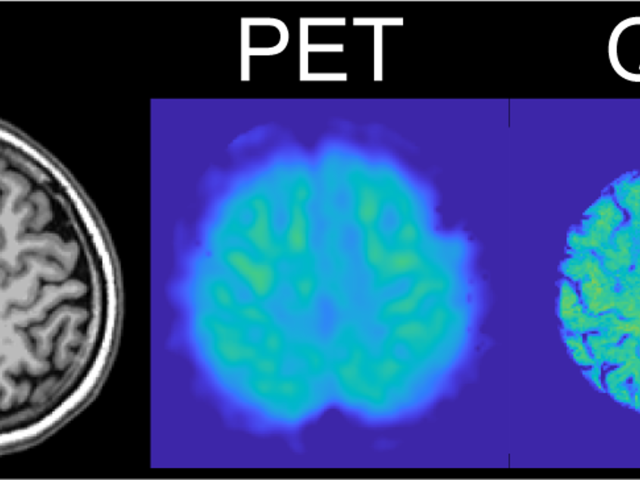
Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a non-invasive imaging biomarker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease
The long-term objective of the Wang lab’s research is to establish quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) marker for predicting neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The lab’s scientific premise is that QSM can measure iron overload involved in AD progression. The lab’s approach is to establish QSM as an MRI marker for predicting...
7T magnetic resonance imaging system for basic, translational and clinical research
Weill Medical Medicine (WCM) of Cornell University has requested High-End Instrumentation Grant Program support to purchase a state-of-the-art human whole-body seven tesla (7T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system as a Special Use Instrument (SUI; PAR-19-177). This 7T MRI is part of a major WCM strategic investment in crucial imaging infrastructure needed to advance basic, translational and...
Feasibility of challenge-free QSM based quantitative mapping of cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen
The objective of this proposed research is to develop a noninvasive, easily accessible and widely usable imaging method to map the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (CMRO2). Oxidative metabolism is the main source of energy for proper human brain function. Consequently, brain tissue is highly susceptible to damage associated with oxygen deficiency, including hypoxia in Alzheimer’s...
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for the study of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Award or Grant: The Leon Levy FoundationIn this research project, the Kovanlikaya lab used advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), arterial spin labeling (ASL), phase contrast cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow measurement and structural volumetric MRI to develop quantitative criteria to diagnose normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) patients more...
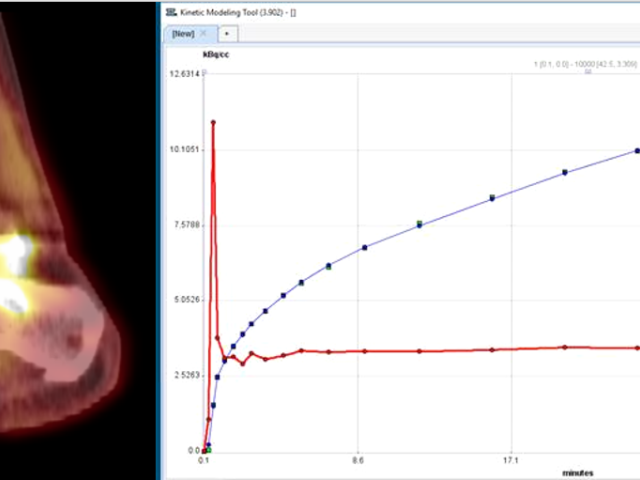
Measurement of bone blood flow and osteoblastic turnover using MRI and PET
Bone blood flow (BBF) and turnover may be altered in many disease states such as osteoarthritis (OA), bone marrow lesions, and trauma or fracture. Dr. Dyke’s group pioneered the use of pharmacokinetic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) modeling of various agents to measure BBF and turnover in disease progression of OA, and following injury. These techniques...
Compact representations of dynamic liver MRI
Award or Grant: R01 CA181566-01A, National Institutes of Health (NIH)The goal of the proposed research is to develop a sensitive and early measurement of treatment response in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent malignant liver cancer. Relevance: This research will result in a quantitative measure of the malignancy of liver cancer, whose burden on the public health is expected to...
Vastly accelerated dynamic spiral MR liver imaging
Award or Grant: R21 DK090690-01A1, National Institutes of Health (NIH) Liver fibrosis and its most advanced stage, cirrhosis, are consequences of chronic and acute hepatic disease. Fibrosis leads to a loss of liver function, and both regional and global perfusion changes. Currently, the gold standard for assessing fibrosis is liver biopsy, which is an invasive technique. The long-term goal is to...
Imaging biomarkers for disease severity and therapeutic response in CLN2 disease
Award or Grant: U54NS065768, BioMarin Pharmaceutical, 190-201, 190-202, 190-203Ceroid lipofuscionosis type 2 (CLN2) disease is a rare, rapidly progressing lysosomal storage disease with severe neurological complications including widespread neurodegeneration. The disease’s rarity, as well as the possibility of non-uniform progression depending on genotype, means that limited data are available...
Novel dynamic liver imaging method with flexible temporal and spatial resolution
Liver cancer is an increasing burden on public health. Currently, a 3D multi-phase contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exam is used to separate the arterial from the venous blood supply to any lesion to determine whether it is malignant or not. It relies heavily on the ability of the patient to sustain a breath-hold, but in a considerable subset of patients, this ability is...
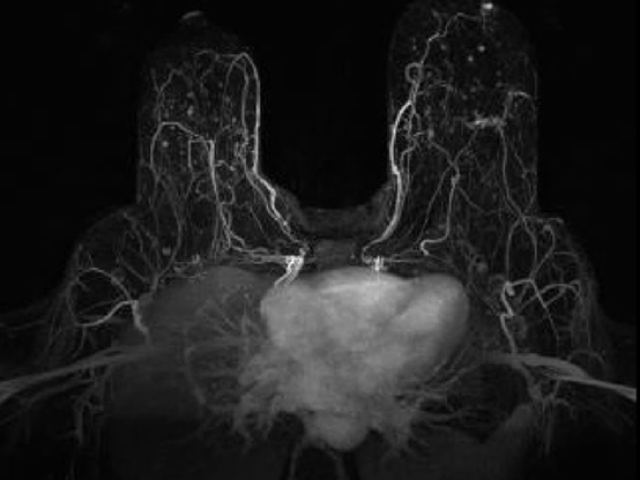
Active contrast encoding (ACE)-MRI study of breast cancer
Awards or Grants: R01 CA160620, National Cancer Institute (NCI), 2/1/2019-1/31/2024Description: Assessment of cancer treatment requires an effective non-invasive method of measuring both the vascular and cellular changes induced by therapies. The Kim team’s underlying hypothesis is that a single dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurement, using the active...