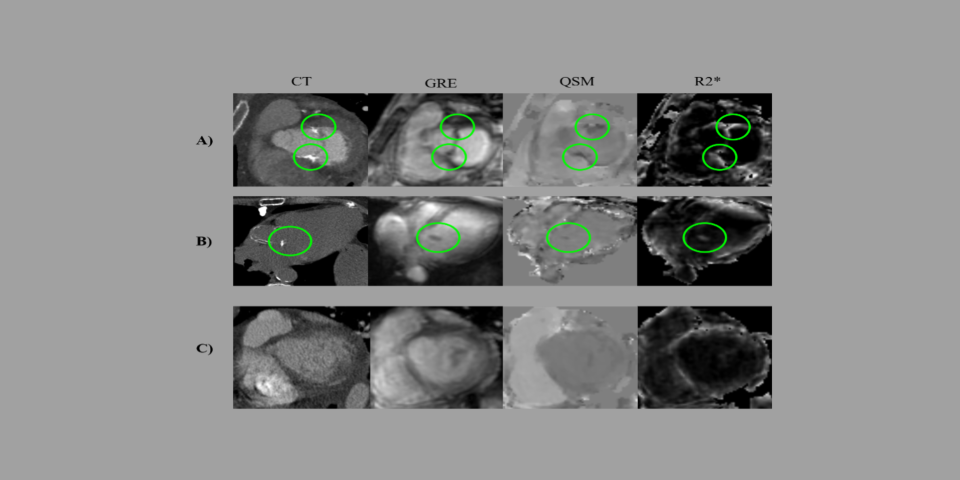
The goal of this research is to develop cardiac quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), a new magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique, for non-invasive measurement of blood oxygen saturation in the heart—an index that strongly predicts clinical outcomes but currently requires invasive testing. To do so, blood oxygenation on QSM will be validated in relation to invasively measured oxygenation, effort tolerance and clinical outcomes in patients with pulmonary hypertension (a condition in which low blood oxygen is common).
Relevance: Results will address key technical and clinical knowledge gaps regarding blood oxygen measurement by cardiac QSM toward the goal of early diagnosis, therapeutic optimization and improved outcomes for patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Techniques used: MRI acquisition, reconstruction and post-processing, MRI pulse sequence development, accelerated imaging, deep learning, biophysical modeling, QSM, MRI relaxation rate mapping, pressure measurements, cardiac catheterization, clinical research, cardiac output, six-minute walk test