LUCINDA: Leuprolide plus Cholinesterase Inhibition to reduce Neurologic Decline in Alzheimer’s
LUCINDA is a clinical trial to determine whether Leuprolide (Eligard®, an injectable medication) can slow or prevent decline in thinking abilities and functioning in women with Mild Cognitive Impairment or Alzheimer’s Disease who are also taking the medication donepezil (Aricept®, a cholinesterase inhibitor.) LUCINDA is taking place at three sites in the United States: Weill Cornell Medicine in...
Imaging mass spectrometry to identify key early changes in lipid metabolism of AD mouse models
The McIntire lab is studying changes in the brain lipidome using targeted liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) and untargeted imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) resulting in a system-wide, publically available lipid map. Data from the lab show distinct regional distribution of acyl chain lipid species across mouse brains using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry...
Generation of a mouse strain that ameliorated behavioral deficits despite amyloid accumulation
This project involved the generation of a novel mouse strain that ameliorated phosphoinositide depletion and behavioral deficits despite the continued accumulation of amyloid.
The effects of iron on oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s biomarkers in amyloid-positive and negative elderly individuals
Award or Grant: R01, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute on Aging (NIA) (2020-2025)Preclinical and postmortem studies have shown that iron colocalizes with beta-amyloid plaques, and iron dyshomeostasis can lead to free radical formation and neuronal loss. Using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), and fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s...
Novel algorithms for reducing radiation dose of CT perfusion
Award or Grant: R44, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) (2017-2022)This study will optimize and validate a k-space weighted image average algorithm for reducing dose of computed tomography (CT) perfusion images.
Predictive model of spread of Parkinson's pathology using network diffusion
Award or Grant: R01, National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) (2016-2021)This study will aim to use brain connectivity to quantitatively model the spread of Parkinson’s disease pathology using a novel “network diffusion” model, based on in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of patients.
Effects of traumatic brain injury and posttraumatic stress disorder on Alzheimer’s disease in veterans using the Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (ADNI-DoD)
Award or Grant: Department of Defense (2013-2018)The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative of the Department of Defense (ADNI-DoD) was a multicenter, observational study to determine the effects of traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSD) in veterans on subsequent development of brain amyloidosis and Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Effects of Type 2 diabetes and glycemic control on brain amyloid deposition in nondemented adults
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) (2013-2015)This study investigated the relationships between (1) insulin resistance and brain amyloidosis and, (2) oxidative stress and brain amyloidosis in nondemented individuals, using magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy and amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) scans with...
Multimodal imaging of apolipoprotein E epsilon 2 carriers
Award or Grant: National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) Clinician-Scientist T32 Training Grant in Biomedical Imaging (2009-2010)This study used multimodal imaging techniques (voxel-based morphology, arterial spin labeling perfusion, and diffusion tensor imaging) to characterize the effects of the APOE e2 allele on the brain. The APOE...
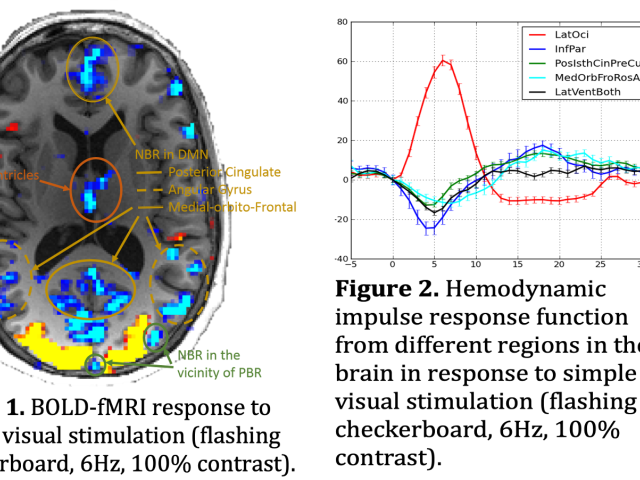
Negative bold response
The Quantitative Neuroimaging Laboratory’s (QNL’s) main research project is investigating the neural and neurophysiological mechanisms underpinning the negative blood-oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) response (NBR). Emerging evidence sheds light on the mechanism underlying the task-based positive BOLD response; however, the accompanying NBR is mostly unknown (Bentley et al.: 2016; Hayden et al...